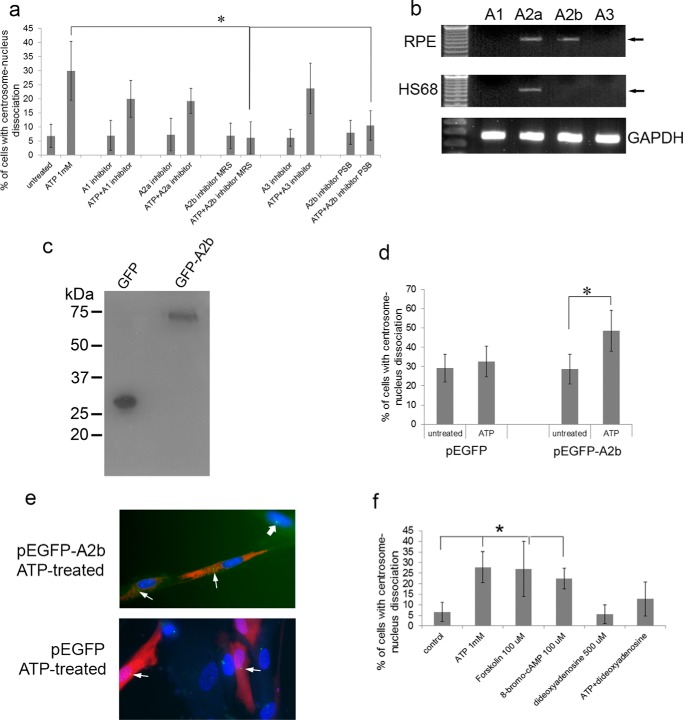
FIGURE 3.
The A2b receptor is required for ATP induced centrosome-nucleus separation. Our data suggested that one of the P1 purinergic adenosine receptors is involved in mediating the observed ATP effect. a, RPE cells were treated for 18 h with the indicated compounds alone or in combination with 1 mm ATP. The concentrations used for the inhibitors were as follows: A1 inhibitor, 40 μm PSB36; A2a inhibitor, 20 μm SCH58261; A2b inhibitor MRS, 40 μm MRS1754; A2b inhibitor PSB, 40 μm PSB1115; and A3 inhibitor, 40 μm MRS1523. Untreated and treated cells were analyzed for centrosome-nucleus separation as described above. Data were collected from three independent assays, for each of which 300 cells were analyzed. b, RT-PCR analysis of A1, A2a, A2b, and A3 mRNA expression in RPE and HS68 cells. c, Western blotting analysis of HS68 cells, which lack A2b, transfected with pEGFP (as a control) and with pEGFP-A2b expressing a GFP-A2b fusion protein. d, HS68 cells transfected with pEGFP or with pEGFP-A2b were left untreated or treated with 2 mm ATP for 17 h, and the distance between the centrosome and nucleus was analyzed as described above. Data were collected from three independent assays, for each of which 300 cells were analyzed. e, example of HS68 cells transfected with EGFP or EGFP-A2b and treated with ATP. Thin arrows point to centrosomes in transfected cells, and the thick arrow points to a centrosome in an untransfected cell. f, RPE cells were treated with two adenylate cyclase activators (100 μm forskolin, 100 μm 8-bromo-cAMP) or with an adenylate cyclase inhibitor (500 μm dideoxyadenosine). ATP alone was used as a control for separation. Untreated and treated cells were analyzed for centrosome-nucleus separation as described above. Data were collected from three independent assays, for each of which 300 cells were analyzed. *, p < 0.05.