FIGURE 5.
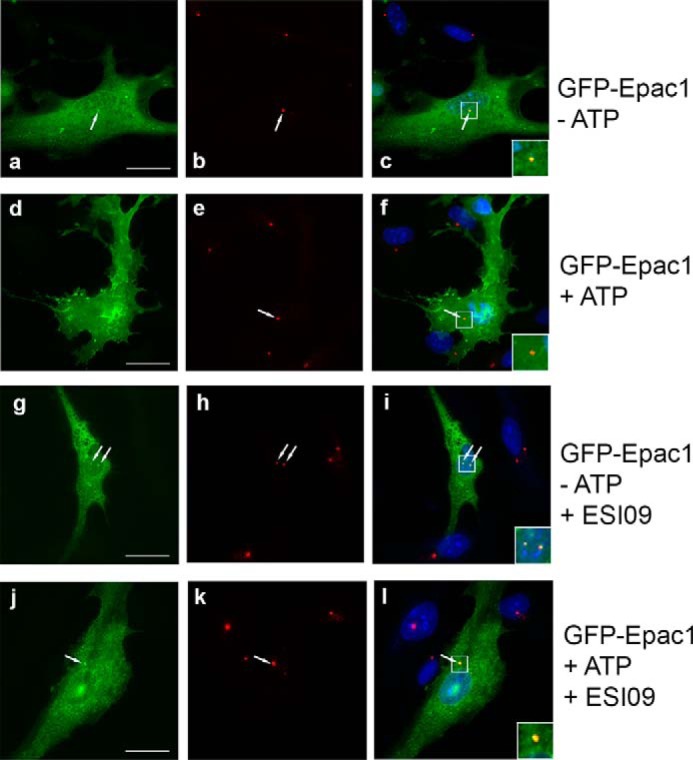
Centrosomal localization of Epac1 is lost upon ATP treatment. To analyze Epac1 localization, we employed GFP-Epac1 (a, d, g, and j), which had been used extensively for localization studies. b, e, h, and k show pericentrin on the centrosome. c, f, i, and l show merged images. a–c, localization of Epac1 in the cytosol, on the nuclear membrane, and on the centrosome (arrow) in untreated cells. Inset, an enlarged image of the centrosome (yellow). d–f, ATP treatment causes significant translocation of Epac1 to the plasma membrane, and Epac1 can no longer be detected at the centrosome (the inset shows a red centrosome). g–i, without ATP, Epac1 localization at the centrosome is not affected by the Epac1 inhibitor ESI09 (the inset shows yellow centrosomes). j–l, the Epac1 inhibitor ESI09 prevents loss of Epac1 at the centrosome (the inset shows a yellow centrosome) and blocks translocation to the plasma membrane. Scale bar = 20 μm.
