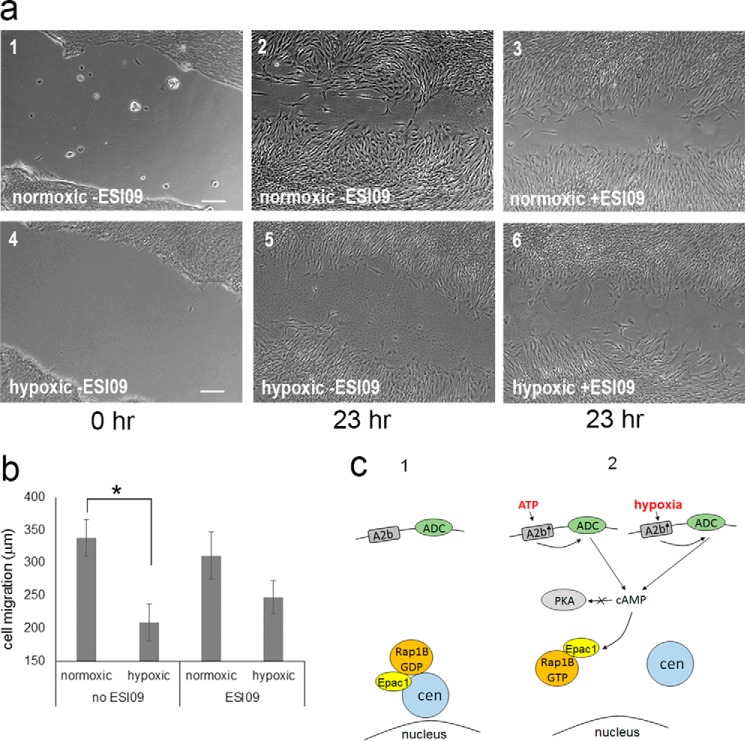
FIGURE 8.
Hypoxia reduces cell migration via the A2b-Epac1 pathway. a, RPE cells were grown under normal conditions (normoxic, 1–3) and reduced oxygen conditions (hypoxic, 4–6). After 48 h, the cell scratch assay was performed, and cells were observed immediately (1 and 4) and after 23 h (2, 3, 5, and 6). Cell migration was measured for untreated cultures (−ESI09; 1, 2, 4, and 5), and cultures were treated with the Epac1 inhibitor ESI09 (3 and 6). b, quantitation of data obtained in scratch assays as shown in a. Data were collected from four independent assays, for each of which 20 distance points were analyzed. c, a model comparing the normal state (1) and the activation of the A2b-Epac1 pathway (2) for ATP treatment and hypoxia. Indicated are the critical players A2b, Epac1, and Rap1B (GDP or GTP-bound). ADC, adenylyl cyclase; cen, centrosome. *, p < 0.05.