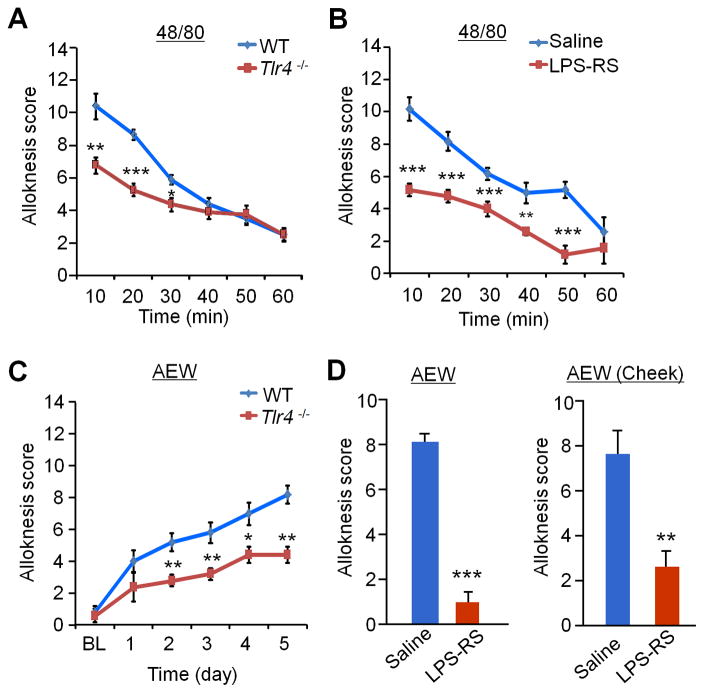
Figure 2. Alloknesis under both acute and chronic itch conditions is impaired in Tlr4−/− mice and suppressed by intrathecal LPS-RS in the back and cheek models.
(A) Alloknesis, induced 30 min after compound 48/80 (48/80) injection, is partially reduced in Tlr4−/− mice. (B) Alloknesis, induced 30 min after 48/80 injection, is suppressed by intrathecal injection of LPS-RS (20 μg). (C) Alloknesis, induced after AEW-induced dry skin, is partially reduced in Tlr4−/− mice. (D) AEW-induced alloknesis at Day 6 in either neck model or cheek model is suppressed by intrathecal LPS-RS (20 μg). Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, compared with WT mice or saline vehicle group, Student’s t test; n = 5–6 mice per group.