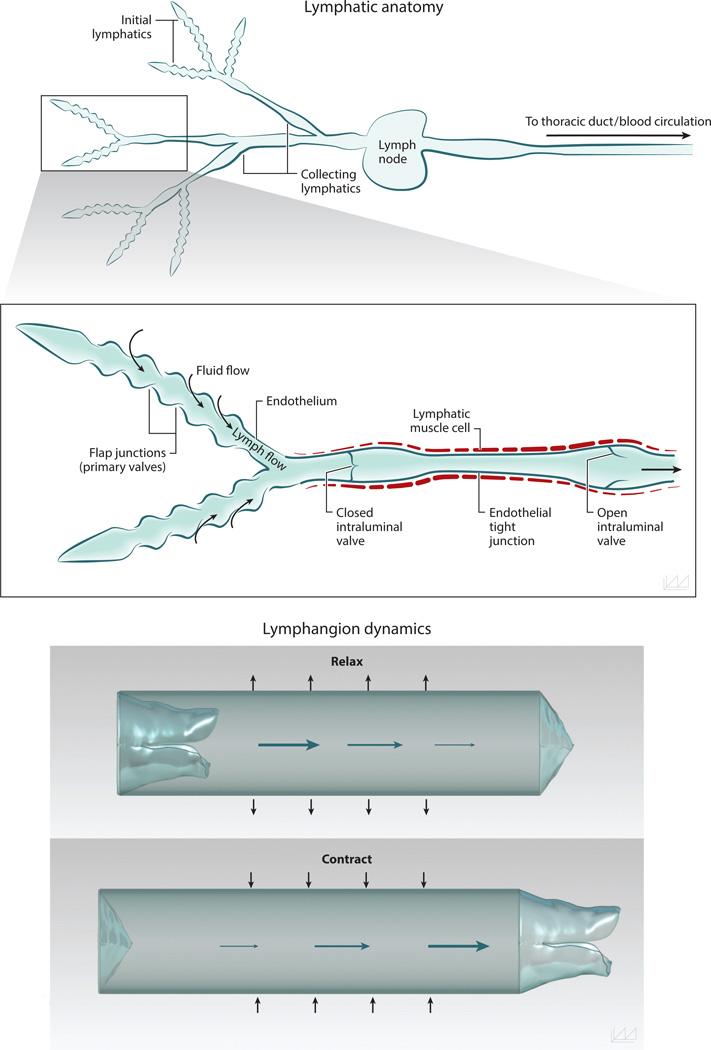
Figure 1.
Anatomy of the lymphatic network and valve function. The lymphatic network consists of initial lymphatic vessels, which are responsible for collecting interstitial fluid to create lymph, and collecting lymphatic vessels, which carry fluid from the peripihfery to lymph nodes. The endothelial cells of initial lymphatic vessels overlap one another to create one-way valves, enabling cell- and pressure-driven fluid entry. The collecting lymphatic vessels are invested in specialized lymphatic muscle cells that contract to drive flow. Intraluminal valves in the collecting lymphatic vessels are critical to preventing backflow. The vessel segment between two valves is called a lymphangion and is the primary pump for lymph flow.