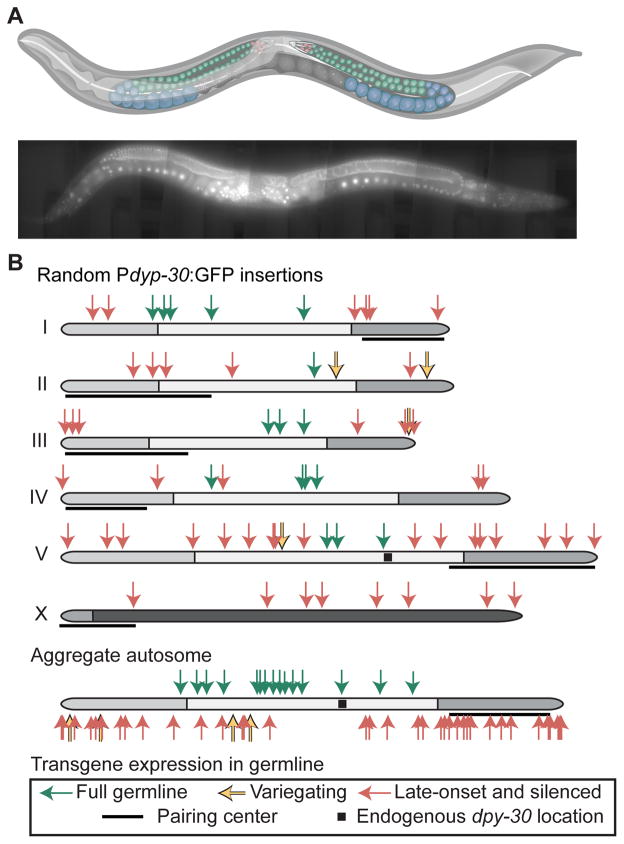
Figure 1. Many Pdpy-30:GFP transgenes are specifically silenced in the germline.
A. Top. Schematic of C. elegans hermaphrodite with the female germline highlighted. Red = mitotic cells; green = early meiotic cells; blue = late meiotic cells. Bottom. Composite fluorescence image of animal expressing a Pdpy-30:GFP transgene (42x magnification, scale bar = 50 micron). Graphic of C. elegans modified from “Caenorhabditis elegans hermaphrodite adult-en.sv” by K.D. Schroeder from Wikimedia Commons under a CC-BY-SA 3.0 license.
B. Top. Germline expression at 25°C of Pdpy-30:GFP transgenes inserted randomly by Mos1 transposition. Genomic insertion sites, transgene copy number, and somatic expression of all insertions were previously verified (Frøkjær-Jensen et al., 2014). Germline fluorescence is indicated by colored arrows (key at bottom. Black squares indicate the endogenous location of dpy-30, gray shading indicates enrichment of repressive histone modifications (Liu et al., 2010), and pairing centers are indicated with black lines (MacQueen et al., 2005). Bottom. Aggregated normalized autosomes aligned with pairing centers to the right and Pdpy-30:GFP insertions.
See also Figure S1 and Table S2 for details of classification.