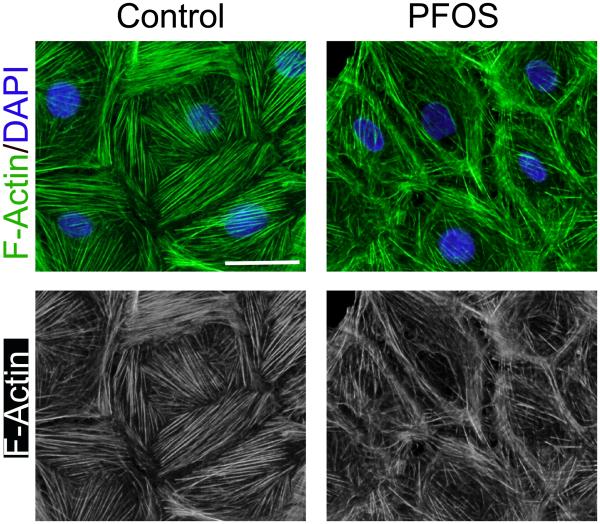
Figure 2. Actin microfilaments in rat Sertoli cells cultured in vitro and changes in their organization following treatment with PFOS.
Sertoli cell isolated from 20-day-old rat testes were cultured in serum-free F12/DMEM supplemented with growth factors for 4 days. Distinctive actin microfilaments (green fluurescence) that stretch across the Serotli cell are noted. However, following treatment of these Sertoli cells with PFOS at 20 μM for 24 hr, actin microfilaments are truncated. Thus, defragemented actin microfilaments no longer capable of supporting adhesion complexes, such as occludin-ZO-1 and N-cadherin-β-catenin, to confer cell adhesion, thereby destablizing the Sertoli cell FJ-permeability barrier function, facilitating the entry of additional toxins to the adlluminal compartment behind the BTB. The net result thus leads to Sertoli cell and testicular injury. The bottom panel is the black-and-white microgaphs of the green fluorescence microgaphs shown in the top panel, better illustrating the actin microfilaments. Scale bar, 20 μm, which applies to other micrographs.