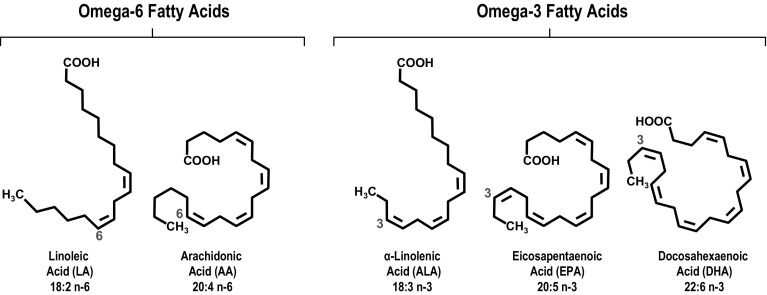
Fig. 1.
Structures of omega-3 fatty acids. Both omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids, meaning that the hydrocarbon chain contains multiple double bonds. The naming convention is [number of carbon atoms]:[number of double bonds], n- (or ω)-[position of first double bond starting from the methyl end of the chain, shown in red]. Omega-3 fatty acids generally have anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic properties, whereas omega-6 fatty acids generally have pro-inflammatory and pro-thrombotic properties