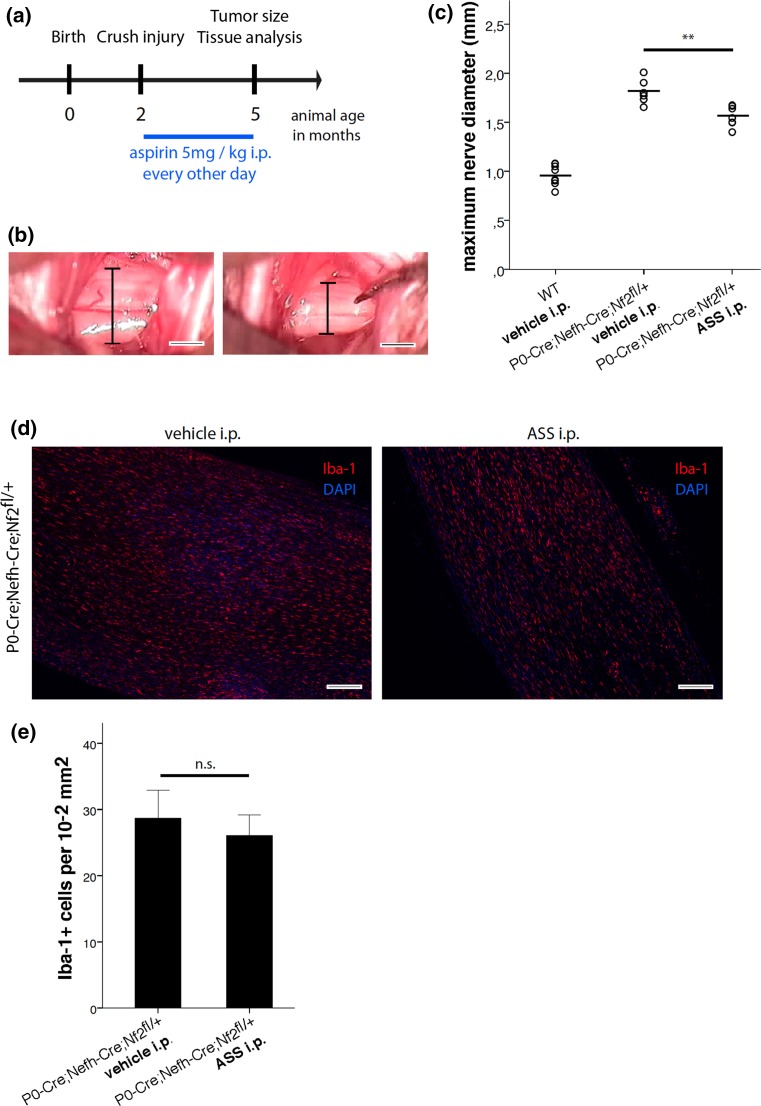
Fig. 9.
Systemic aspirin administration decreases schwannoma progression in P0-Cre;Nefh-Cre;Nf2fl/+ mice. a Schematic representation of the aspirin (ASS) treatment protocol. b Representative images showing the method for in situ tumor size quantification. The crushed sciatic nerve was exposed surgically in order to assess the maximum sciatic nerve diameter following as indicator for tumor size. c Quantification of maximum sciatic nerve diameters in wild type (WT) and P0-Cre;Nefh-Cre;Nf2fl/+ mice, 3 months after crush injury. Mice received systemic administration of either medium-dose aspirin (5 mg per kg ASS i.p.) or vehicle (**P < 0.01; n = 7 mice per genotype; mean ± SD). d Longitudinal sciatic nerve sections were prepared from vehicle or aspirin-treated P0-Cre;Nefh-Cre;Nf2fl/+ mice 3 months after crush injury and immunohistochemically stained for the macrophage marker Iba-1 (red). DAPI counterstaining indicates cell nuclei (blue). Scale bars represent 200 μm. e Quantification of Iba-1-positive cells nerve tissue 3 months after crush injury, taken from aspirin and vehicle-treated P0-Cre;Nefh-Cre;Nf2fl/+ mice (n.s. not significant; n = 3 nerves per genotype; mean ± SD)