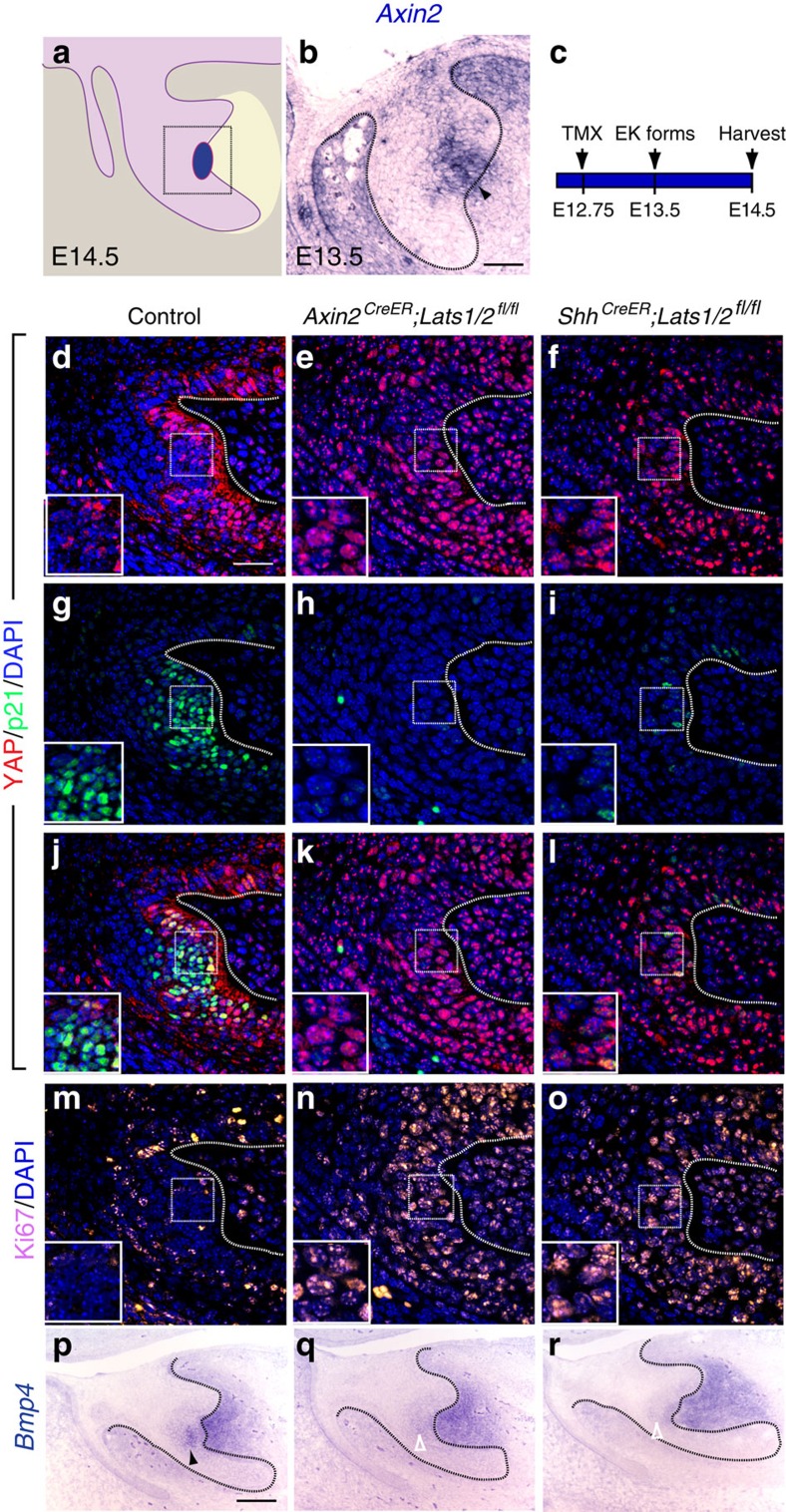
Figure 3. Proper YAP localization is essential for the formation of EK during tooth development.
(a) Schematic diagram of an E14.5 incisor tooth germ. Square box represents areas imaged in d–o. (b) In situ hybridization of Axin2 at E13.5 tooth germ (arrowhead indicates the expression of Axin2 in the EK). (c) Time course for treatment of Axin2CreER;Lats1/2fl/fl and ShhCreER;Lats1/2fl/fl embryos with tamoxifen to delete Lats1 and Lats2 in the EK. (d,g,j,m) In the EK, YAP is excluded from the nucleus with increased p21 and decreased Ki67 expression at E14.5. (e,f) Double deletion of Lats1 and Lats2 with EK-specific Axin2CreER and ShhCreER induces the nuclear localization of YAP. (h,i) Double deletion of Lats1 and Lats2 with EK-specific Axin2CreER and ShhCreER decreases p21 expression. (k,l) Overlay images of YAP and p21 staining. (n,o) Double deletion of Lats1 and Lats2 in the EK induces ectopic cell proliferation, as shown by Ki67 staining. (p) In situ hybridization of the EK marker Bmp4 at E14.5 (black arrowhead). (q,r) Double deletion of Lats1 and Lats2 inhibits Bmp4 expression (open white arrowheads). Dotted lines outline the tooth germ epithelium in b–r. Scale bar, 50 μm (b,c); 25 μm (d–o); 100 μm p–r).