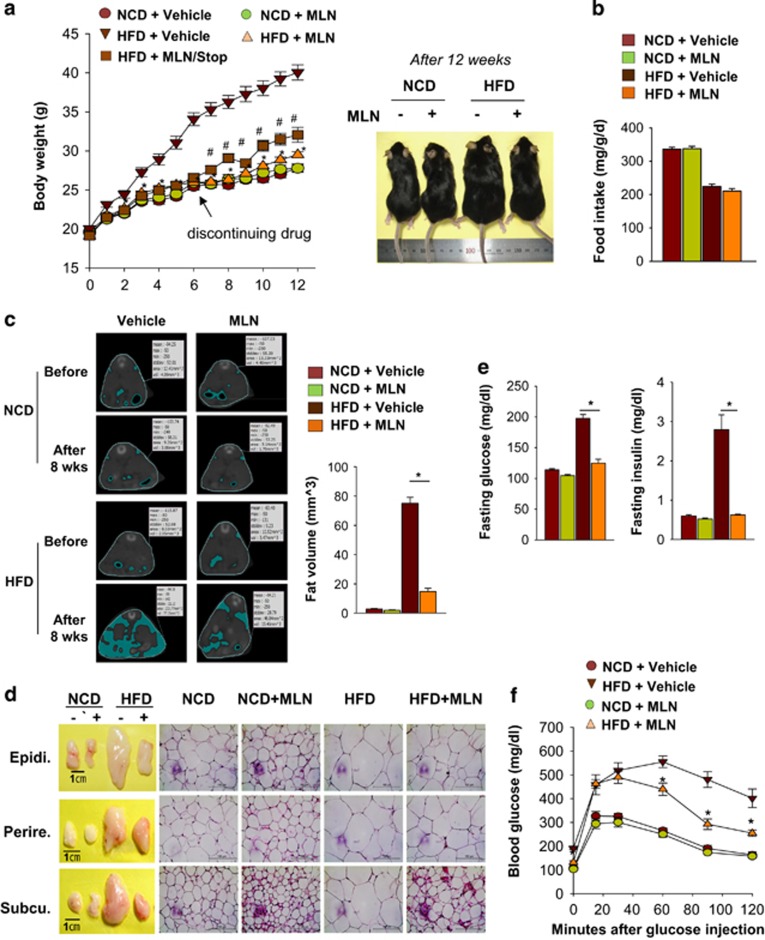
Figure 7.
MLN4924 prevents obesity and glucose intolerance induced by high-fat diet. (a) MLN4924 prevents excess gaining of weight in mice fed with HFD. Mice were divided into five groups (n=8 per group): vehicle treatment in NCD-fed mice and HFD-fed mice, MLN4924 treatment (30 mg/kg) in NCD-fed mice and HFD-fed mice, and MLN4924 withdrawal after 6 weeks treatment in HFD-fed mice. All mice were weighed every week and the body weights (mean±S.E.M.) are plotted as a function of time (left panel). Mice were photographed on the 12th week (right panel). (b) Weekly food intakes of the mice were monitored and the amounts (mean+S.E.M., n=8) are plotted. (c) MLN4924 reduces the volume of abdominal fat tissues. Representative CT images from the optimal single slice with both renal hila are presented (left panel). Mice underwent a CT scan before and after HFD feeding with vehicle or MLN4924 treatment. The volumes of abdominal fat tissues (mean+S.E.M., n=8) were calculated based on three-dimensional CT images (right panel). *P<0.05. (d) MLN4924 prevents HFD-induced overgrowth of fat tissues in mice. Gross appearance (left panel) and hematoxylin and eosin-stained microscopic pictures (right panel) of mouse epididymal, subcutaneous, and perirectal fat tissues and staining of these fat tissues are presented. (e) MLN4924 reduces the burden of insulin in HFD-fed mice. After 12 h of fasting, glucose and insulin levels were measured in serum. All data are presented as the means+S.E.M. (n=8). *P<0.05. (f) MLN4924 ameliorates HFD-induced glucose intolerance. Glucose was administered intraperitoneally after 12 h fasting, and then serum glucose levels (mean±S.E.M., n=8) were measured at the indicated time