Figure 4.
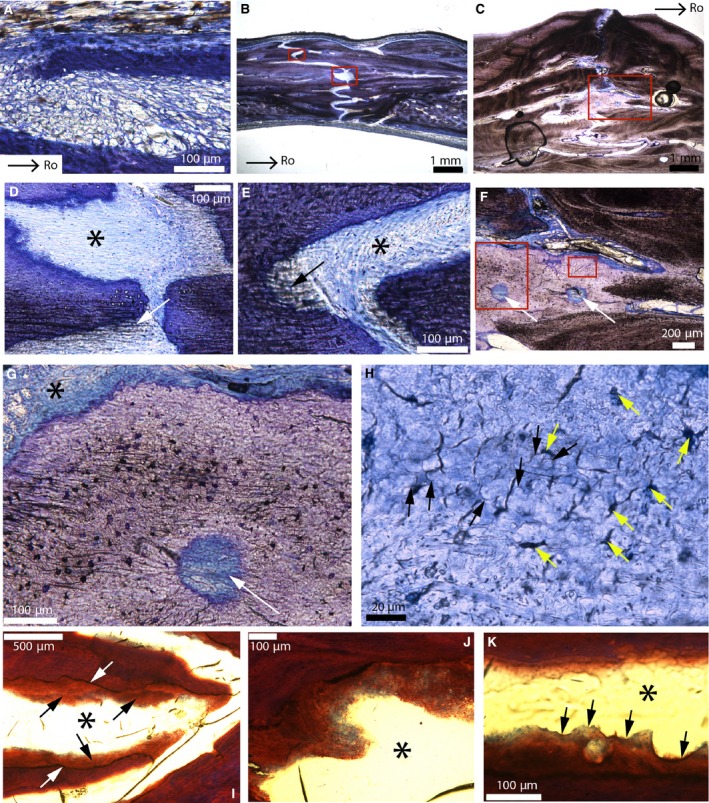
Parasagittal sections of the fronto‐parietal suture of American alligators stained with toluidine‐blue (A–H) and Masson's trichrome (I–K). (A) Fronto‐parietal suture of Alligator 1. It appears to be formed of mesenchyme. (B) Fronto‐parietal suture of Alligator 3. (C) Ectocranial part of the fronto‐parietal suture of Alligator 6. (D) Close‐up of the lower red box in (B). Thick collagen fiber bundles are continuous between the bone and the suture (white arrow). The black asterisk shows a uniform dense fibrous tissue (with blue fibroblast nuclei). This suture lacks a periosteum. (E) Close‐up of the upper red box in (B). Once more, thick collagenous fibers can be seen (black arrow), as well as a uniform sutural layer (black asterisk). (F) Close‐up of the red box in (C). A light purple tissue is found right at the sutural borders. It possesses two vascular canals (white arrows). (G) Close‐up of the right red box in (F), showing a vascular canal (white arrow) bordered by different zones: cellular, acellular, fibrous and non‐fibrous. The cellular zones show cellular lacunae resembling plump osteocytes with canaliculi. (H) Close‐up of the left red box in (F). In areas that appear acellular, this tissue shows globular structures (black arrows) and dark spaces of various shapes (yellow arrows). These spaces do not have the appearance of regular osteocyte lacunae and they show no evidence of canaliculi. (I) Adjacent section of this same suture in Alligator 6 (black asterisk) stained with Masson's trichrome. Interdigitations are ‘covered’ by this same tissue (black arrows). The core of the interdigitations does not stain like this tissue (see the clear limits indicated by the white arrows). (J) Close‐up of this tissue from another area in this same section. It shows shades of blue and red, while the core of the interdigitations only stains red. The suture is indicated by the black asterisk. (K) Another area in this section shows that this tissue is mineralized as it shows Howship's lacunae (black arrows). The suture is indicated by the black asterisk. Images (A and B) are modified from Bailleul et al. (in press). Images (C, F–H) were reversed for consistent orientation. Abbreviations: same as previous figure.
