Figure 9.
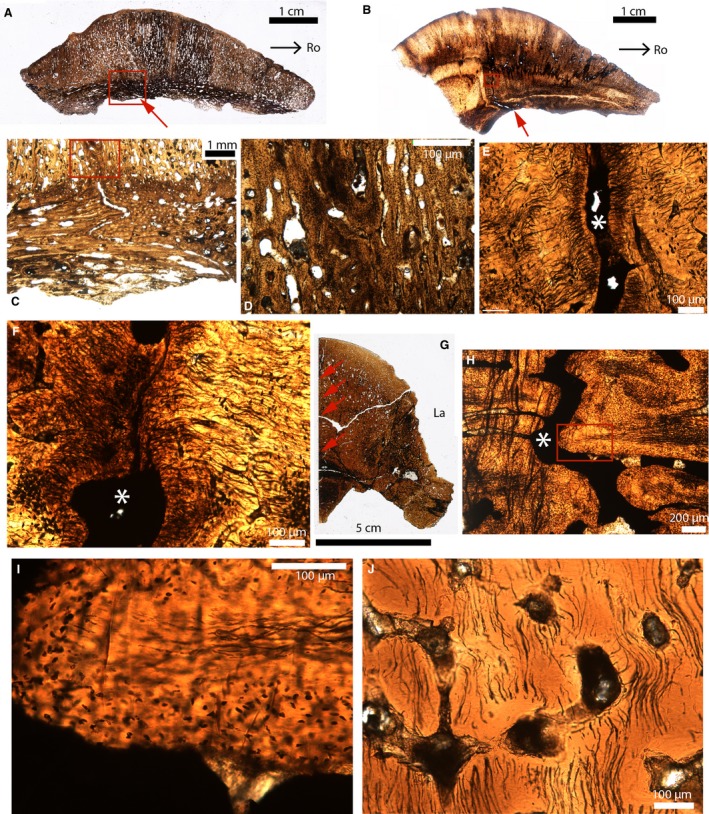
Paleohistological parasagittal sections (A–F) and cross‐sections (G–J) in the cranial domes of some pachycephalosaurids. (A) Whole section of the fronto‐parietal dome of Stegoceras (UCMP 130049). The endocranial part of the suture is indicated by the red arrow. The ectocranial part of this suture is obliterated. (B) Whole section of the fronto‐parietal dome of a Pachycephalosauridae indet (TMP 1974.10.74). The endocranial part of the suture is indicated by the red arrow. The ectocranial part of this suture is obliterated. (C) Close‐up of the red box in (A). (D) Close‐up of the red box in (C). (E) Close‐up of the red box in (B). The suture is indicated by the white asterisk. (F) Close‐up of another area in (B), showing an obliterated suture with two fusing fronts composed of a highly fibrous tissue. The white asterisk indicates the suture. (G) Whole section of the frontals of a Pachycephalosauridae indet (UCMP 154919). The interfrontal suture is indicated by the red arrows. (H) Close‐up of the interfrontal suture in (G). (I) Close‐up of the red box in (H). The interdigitation is composed of an acellular fibrous tissue in the center and a cellular tissue in the periphery. (J) Section showing acellular bone from a ‘non‐sutural’ area. Images (A–E) were reversed for consistent orientation. La, lateral; Ro, rostral.
