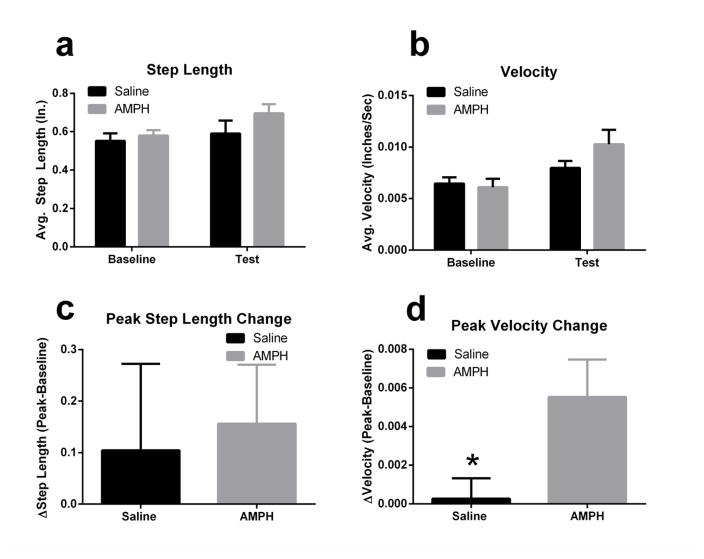
Fig. 3.
Amphetamine (AMPH) 3.2 mg/kg i.p. did not overall change step lengths (a) or velocity of steps (b) as measured by MouseTrapp software when comparing all points prior to treatment and after treatment. When considering only the time points which fell within the maximal effect of AMPH (40–70 min post treatment), a significant increase in step velocity (d), but not length (c) was observed. *p<0.05, 3.2 mg/kg i.p. dose of amphetamine compared to saline treatment.