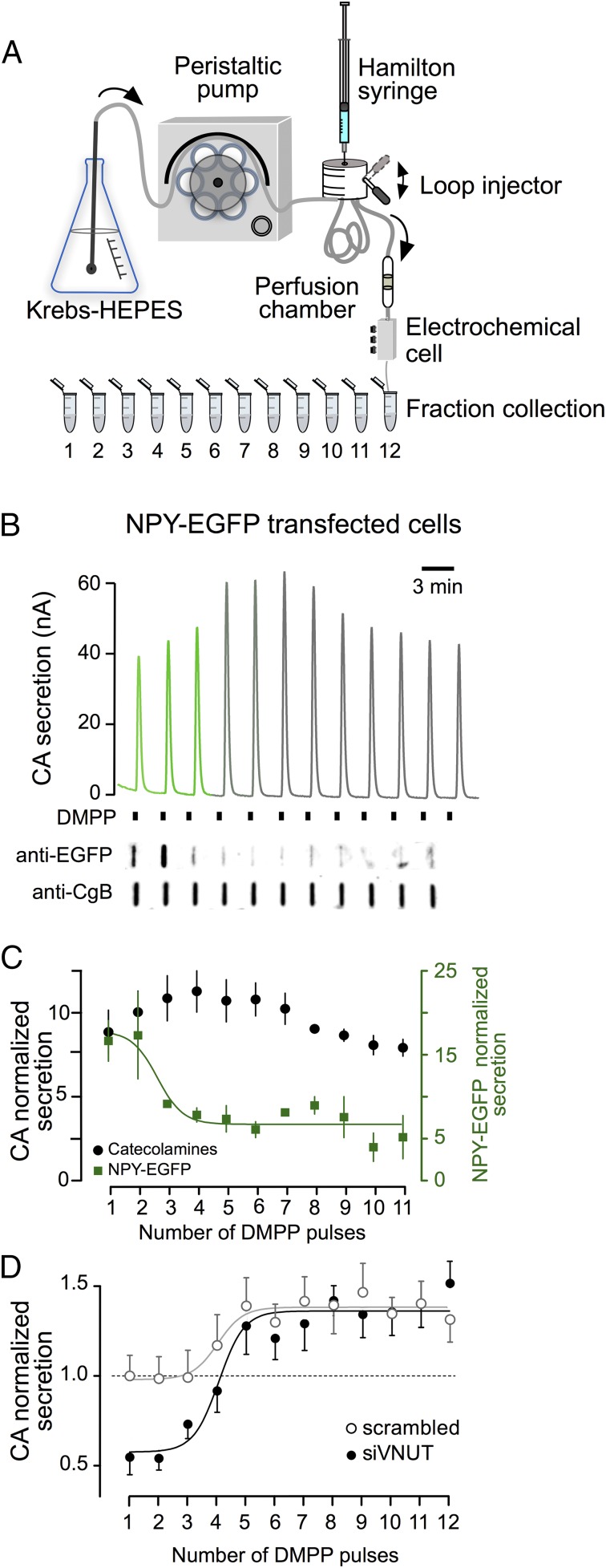
Fig. 4.
VNUT knockdown predominantly affects catecholamine secretion from newly synthesized vesicles. The capacity of cells to recruit vesicles from the early- and late-releasable pools was studied using 12 successive DMPP stimulations. (A) The scheme shows the perfusion system used for the on-line electrochemical analysis of catecholamine release and the fraction collection for protein quantification. (B) Representative traces of the electrochemical recording from perfused chromaffin cells expressing NPY-EGFP. Each current peak indicates catecholamine secretion. A representative dot blot probed for NPY-EGFP and CgB obtained from the same experiment. (C) Time course of catecholamine and newly synthesized NPY (pooled results from four experiments). (D) Time course of catecholamine release from control (scrambled) and knockdown-VNUT (siVNUT) nucleofected chromaffin cells. To correct the bias of different cell batches, the data were normalized to the mean of the first secretory peak from the control cells (scrambled), considering the initial response as 1.