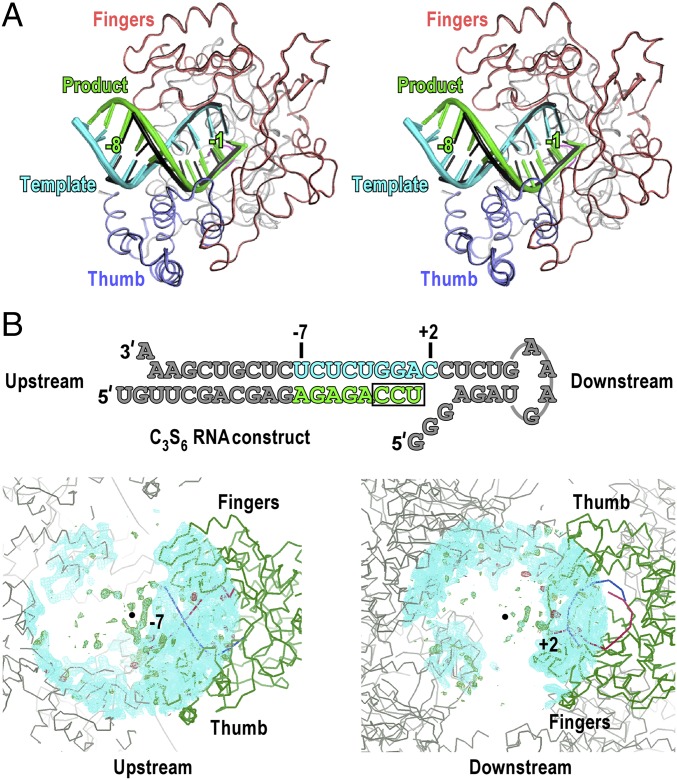
Fig. 4.
The C3S6 complex is a translocation intermediate, has a global polymerase conformation consistent with other complexes, and is free of defined intercomplex interactions at either end of its RNA constructs. (A) Stereo-pair images of all seven complexes with their polymerases superimposed. The C3S6 complex is shown in black, and the other six complexes are colored as the C1S1/2 complex in Fig. 1C. The +2 template nucleotides in all complexes are omitted for clarity. The −1 and −8 position labels correspond to the regular translocational positions defined by the six nontranslocation-intermediate complexes. (B, Upper) The complete sequence of the RNA constructs in the C3S6 complex is shown with gray font indicating unresolved nucleotides in the structure. (Lower Left) A portion of the unresolved upstream RNA backbone in the C3S6 structure is somewhat traceable. (Lower Right) The downstream RNA is essentially disordered. Electron densities for defined crystal contacts are lacking at both ends of the RNA construct. Cyan mesh indicates the 2Fo-Fc electron density map contoured at 1 σ; green/red mesh indicates the Fo-Fc electron density map contoured at 3 σ. Green ribbons indicate polymerase; red/blue ribbons indicate template/product RNA. Black dots indicate the center of the map. The map radius is 30 Å.