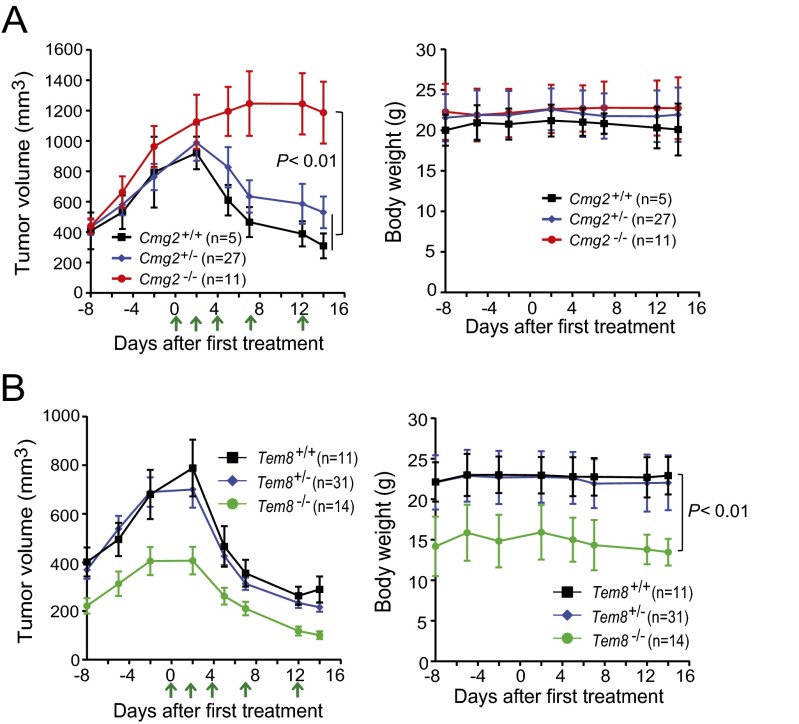
Fig. S3.
The engineered anthrax lethal toxins block A549 tumor growth through the host-derived CMG2 receptor. (A) Littermate Cmg2+/+, Cmg2+/−, and Cmg2−/− athymic nude (Foxn1nu/nu) mice were injected with 1 × 107 per mouse A549 cells. When A549 tumors reached ∼1 cm3, the tumor-bearing mice were treated intraperitoneally with five doses of 15 µg of PA-L1 plus 7.5 µg of LF as indicated by arrows. A slow and moderate response of A549 tumors on Cmg2−/− mice was likely due to the accumulated low toxin activity to A549 cells (Fig. S2B). (B) The A549 tumor-bearing littermate Tem8+/+, Tem8+/−, and Tem8−/− athymic nude (Foxn1nu/nu) mice were treated as in A. Note that the mice were fed the routine hard food and that the Tem8−/− mice exhibited lower body weight than their littermate controls. Tumor volumes, means ± SE; body weights, means ± SD. Student’s t test or one-way ANOVA was used to calculate differences between groups. In A, whereas the tumor volumes of the three groups were not significantly different before the toxin treatment, those of Cmg2+/+ and Cmg2+/− mice were significantly smaller than Cmg2−/− mice after the treatment; P < 0.01, using one-way ANOVA.