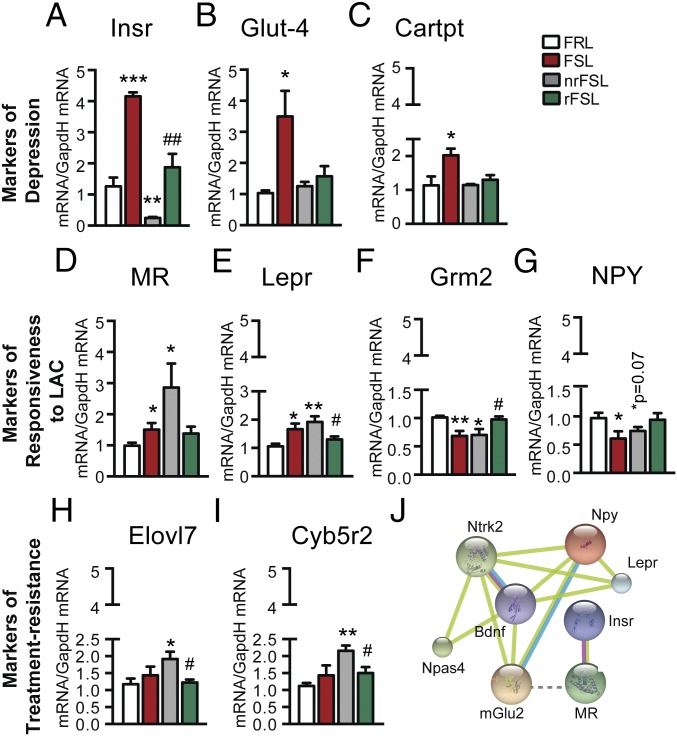
Fig. 4.
Metabolic factors in vDG as important targets of responsiveness to LAC antidepressant treatment, treatment resistance, and depressive-like phenotype. (A–C) qPCR validation confirmed changes in the genes unveiled by RNAseq as markers of the depressive-like phenotype of FSL rats showing up-regulations of Insr, Glut-4, and Cartpt transcripts in the vDG of veh-FSL that were rapidly corrected by LAC in both rFSL and nrFSL. (D–G) qPCR validation confirmed increase in Lepr and MR along with decrease in mGlu2 and NPY in the vDG of veh-FSL as unveiled by RNAseq. Such changes were corrected in rFSL and not in nrFSL after stress. (H and I) The regulators of fatty-acid elongation, Elovl7 and Cyb5r2, emerged as important targets in development of resistance to LAC, low oral dose, in some FSL after stress as confirmed by qPCR validation. (J) Network analysis identifies NPY, among other genes such as BDNF and TrkB (Ntrk2), as critical mediators of the interaction between Lepr and Grm2 (mGlu2: previously identified targets for LAC rapid antidepressant effects). Bars: mean + SEM, *significant comparisons with veh-FRL, #significant comparisons with LAC-treated nrFSL. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01.