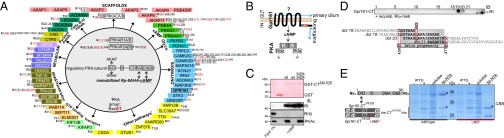
Fig. 1.
PKA phosphoprotein interactome and Gpr161:RI interaction. (A) Phosphoproteins of affinity-purified PKA complexes are listed. Underlining marks previously described p-sites; red labeling highlights PKA group sites with a phosphorylated RxxS/T sequence motif. (B) Schematic illustration of Gpr161 trafficking and PKA signaling; cAMP binds R subunits and activates PKAc. (C) GST pulldown experiments of endogenous PKA subunits from HEK293 cell lysates in the presence or absence of 5 mM cAMP using GST and GST-CT (murine Gpr161-Carboxy-terminus340–528) hybrid proteins. (D) Spotted peptides (25-mers, 15-aa overlap) of human Gpr161-CT were overlaid with recombinant RI. Immunoblotting (IB) has been performed with a monoclonal anti-RI antibody. The helix propensity of this part of Gpr161-CT (flanked by L458 and L477) is shown. Indication of L465. (E) Following bacterial coexpression of his6-tagged CT378–528 (wild-type and L465P) and untagged RIα we purified complexes using Ni-NTA resin. Representative experiment from n = 3. Asterisks (*) indicate specific Coomassie brilliant blue-stained bands.