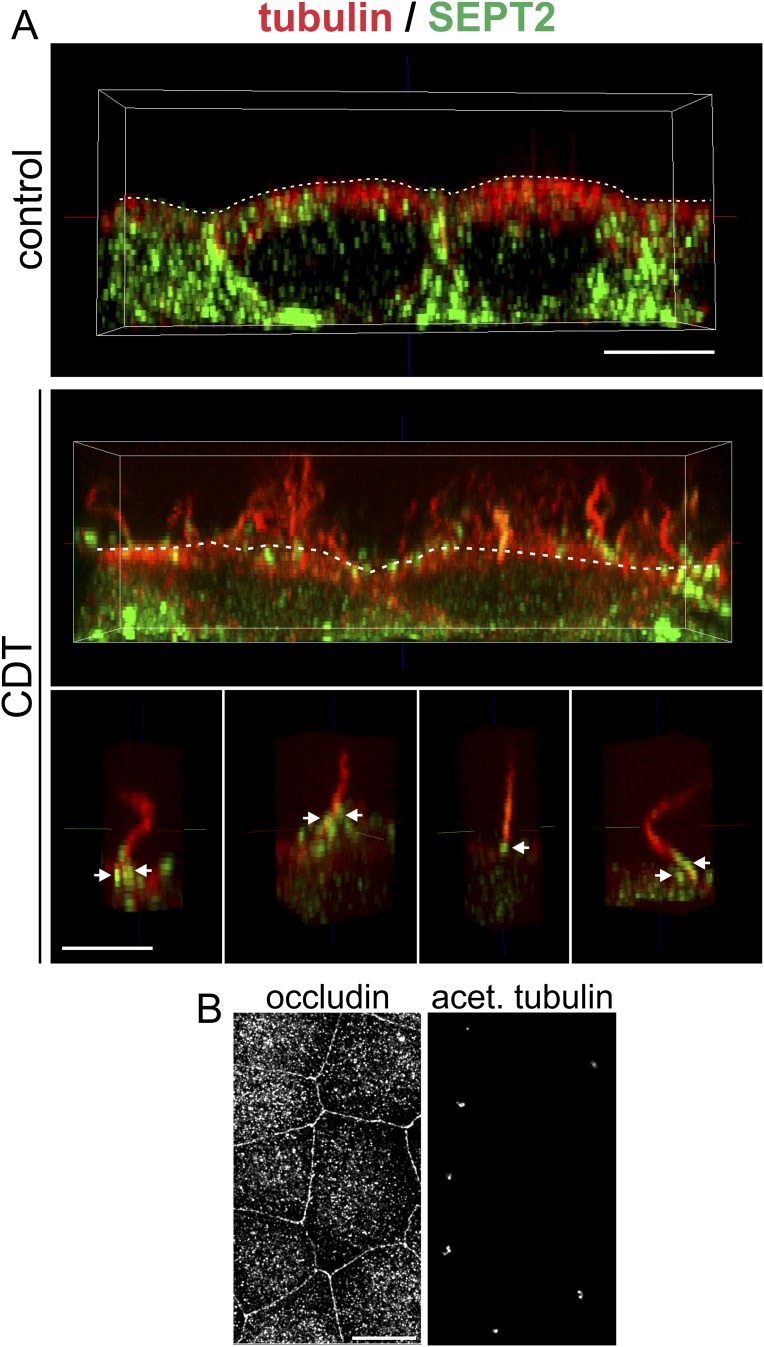
Fig. S4.
Formation of microtubule-based protrusions with septin base in polarized MDCK cells. (A) Indirect immunofluorescence of SEPT2 (green) and α-tubulin (red) in MDCK cells. (Upper) A side view of polarized untreated MDCK cells. (Middle) A side view of CDT-treated (200 ng/mL CDTa and 400 ng/mL CDTb for 90 min) MDCK cells. Above the apical surface (white, dashed line), microtubule-based protrusions have formed in high density. (Lower) A side view of individual microtubule-based protrusions with septin accumulations at their base (white arrows). (Scale bar, 5 µm.) (B) In parallel to the experiment in A, cells were cultured for the same time at the same density. Tight junctions were stained by indirect immunofluorescence for occluding, and cilia were stained by indirect immunofluorescence for acetylated tubulin as markers for differentiation and polarization. (Scale bar, 10 µm.)