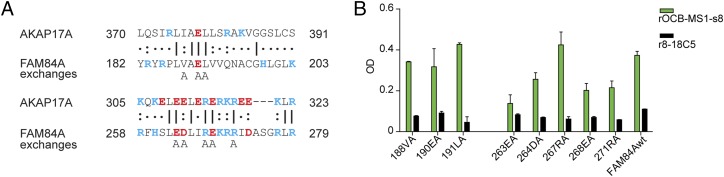
Fig. 5.
Cross-reactivity of rOCB-MS1-s8 between highly homologous epitopes of FAM84A and AKAP17A. (A) Comparison of amino acid sequences of 370–391 (Upper) and 305–323 (Lower) of AKAP17A (upper lines) and 182–203 and 258–279 of FAM84A (middle lines). Identical amino acids are indicated by a dash, highly homologous amino acids by a colon, and similar amino acids by a dot. Positively and negatively charged amino acids are depicted in blue and red letters, respectively. The lowest line indicates which of the FAM84A amino acids were individually replaced by alanine. (B) Recognition of wild-type (FAM84wt) and the eight mutated FAM84A molecules by rOCB-MS1-s8 and the control antibody r8-18C5 as measured by ELISA. Recognition of FAM84A with exchanges of amino acids V188, E190, L191, and R267 to alanine was comparable to the wild-type protein, but considerably reduced by exchanges of amino acids E263, D264, E268, and R271. Data are representative of four independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD.