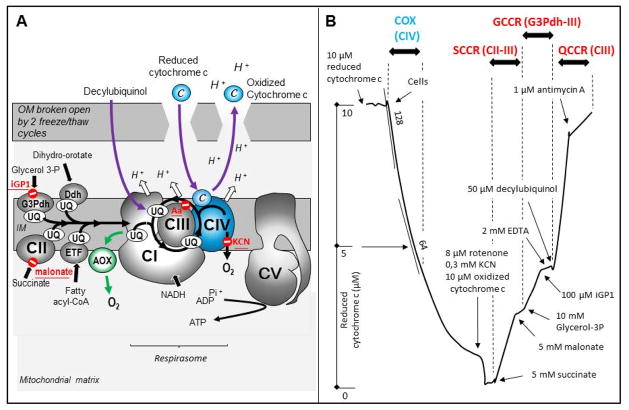
Figure 1. Cytochrome oxidase location in the respiratory chain and activity assay in human skin fibroblasts.
A. Schematic representation of the respiratory chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane showing the interaction of cytochrome oxidase (complex IV) with complexes I and III in a super-complex (respirasome). The site of action of specific inhibitors is indicated in red. The green arrow shows the alternative oxidase (AOX) by-pass, which when expressed in COX-defective human mitochondria or flies rescues their various phenotypes. The assay of COX with externally added cytochrome c requires the permeabilization of the outer membrane. B. Cytochrome oxidase is assayed spectrophotometrically by measuring using a double-wavelength spectrophotometer (550–540 nm) the oxidation of reduced cytochrome c in skin fibroblasts permeabilized by 2 successive freeze/thaw cycles. The reaction is first order with respect to substrate concentration and is thus diminished by half when half of the reduced cytochrome c is consumed. Subsequent sequential addition of rotenone, cyanide, oxidized cytochrome c and succinate measures reduction of cytochrome c, first by the succinate-cytochrome c reductase (CII plus CIII). The activity is essentially rate controlled by CII and can be inhibited by malonate, a competitive inhibitor of CII. Further addition of glycerol-3 phosphate measures the activity from the glycerol-3 phosphate dehydrogenase (G3Pdh) to CIII. This activity can be selectively inhibited by iGP1(143). Finally, addition of decylubiquinol in the presence of EDTA is used to measure antimycin-sensitive CIII activity. Abbreviations: The RC complexes are abbreviated as, CI, CII, CIII, CIV, and the ATP synthase as CV; c, cytochrome c; COX, cytochrome oxidase; Ddh, the dihydroorotate dehydrogenase which catalyze the production of uridine, an essential step for the synthesis of nucleic acids; EDTA, ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid; ETF, the electron transfer flavoprotein involved in the oxidation of fatty acids; G3Pdh, the glycerol 3-phosophate dehydrogenase; GCCR, iGP1-sensitive glycerol 3-phosphate; IM, inner membrane; KCN, potassium cyanide; OM, outer membrane; QCCR, antimycin-sensitive decylubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase; SCCR, malonate-sensitive cytochrome c reductase; UQ, ubiquinone 50, or coenzyme Q10.