Fig. 2.
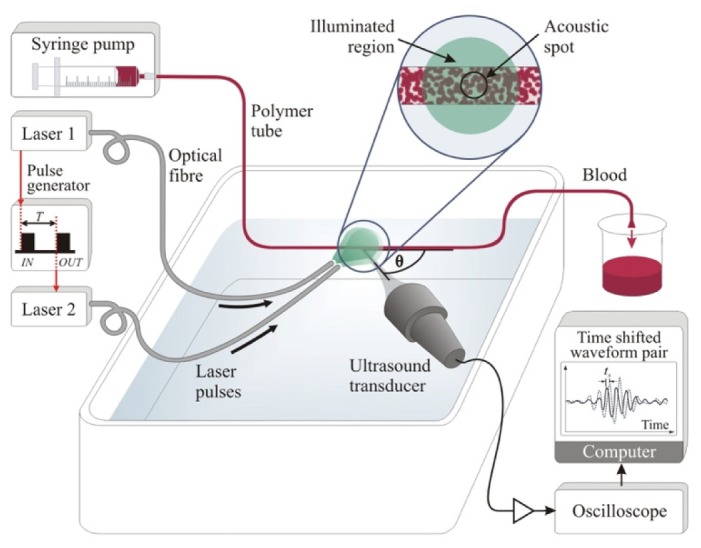
Experimental setup for pulsed photoacoustic Doppler blood flow measurements. Laser pulses separated by a time T are used to generate pairs of photoacoustic waveforms which are detected by an ultrasound receiver positioned at an angle θ to the flow axis. This angle was measured to the nearest degree using a turntable with angular markings at 1° intervals, and verified by horizontally translating the tube and comparing the measured distances with those calculated from cross-correlation of photoacoustic signals acquired before and after translation. The inset shows that whilst a large area (at least 5 mm diameter) of the red blood cells (RBCs) is illuminated, photoacoustic signals are collected from a smaller region defined by the transducer focal spot in order to be representative of the acoustic resolution mode of photoacoustic detection.
