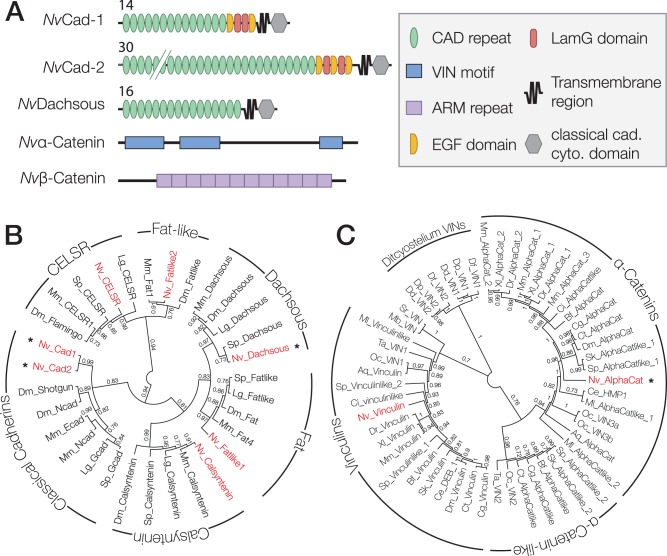
Fig. 1.
Nematostella vectensis has a full complement of CCC components. (A) Predicted domain composition of N. vectensis cadherins, and α- and β-catenin examined in this study. Identified pFam motifs are annotated. Numbers for NvCad-1 and -2 and NvDachsous indicate the number of extracellular cadherin repeats. (B and C) Gene trees for N. vectensis cadherins and α-catenin. Nematostella vectensis genes are in red. Asterisks indicate the proteins examined in this study. Numbers indicate the posterior probability of each branch. Abbreviations for species names are as follows: Aq, A. queenslandica; Bf, B. floridae; Ce, C. elegans; Cg, C. gigas; Ci, C. intestinalis; Ct, C. teleta; Dd, D. discoideum; Df, D. fasciculatum; Dm, D. melanogaster; Dp, D. purpureum; Dr, D. rerio; Lg, L. gigantea; Mb, M. brevicollis; Ml, M. leiydi; Mm, M. musculus; Nv, N. vectensis; Oc, O. carmela; Sk, S. kowalevskii; Sp, S. purpuratus; Sr, S. rosetta; Ta, T. adhaerens; Xl, X. laevis. (B) A consensus phylogeny of the N. vectensis cadherins that cluster within known cadherin sub-types from bilaterian organisms generated using FastTree2. (C) A phylogeny of α-Catenin and Vinculin orthologs from metazoan organisms and related unicellular eukaryotes.