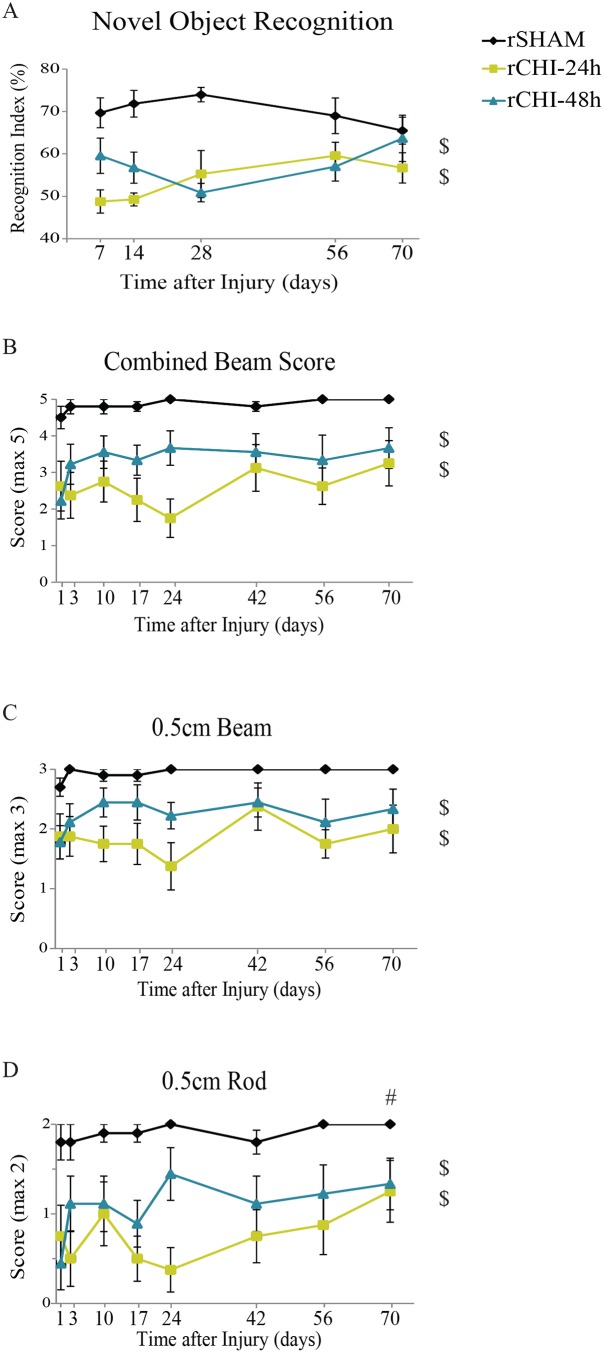
Fig 1. Repeated closed head injury (CHI) induced motor and memory deficits over 10wks post-injury.
Behavioral testing was conducted following repeated sham (rSHAM), repeated CHI at a 24h interval (rCHI-24h), and repeated CHI at a 48h interval (rCHI-48h). (A) Memory scores in the novel object recognition task were calculated by dividing the time spent exploring the novel object by the total exploration time (recognition index). (B) The beam walking task was used to identify deficits in motor coordination. A score of 5 indicated perfect performance on the task, with lower scores indicating poorer motor skills. Component analysis for the beam walking task of (C) the 0.5cm plexiglass beam and (D) the 0.5cm wooden dowel rod. $ indicates significant difference from rSHAM (p<0.05 post-hoc testing for main effect of injury). # indicates that performance across all groups was better at 10wks compared to 24h (p<0.05).