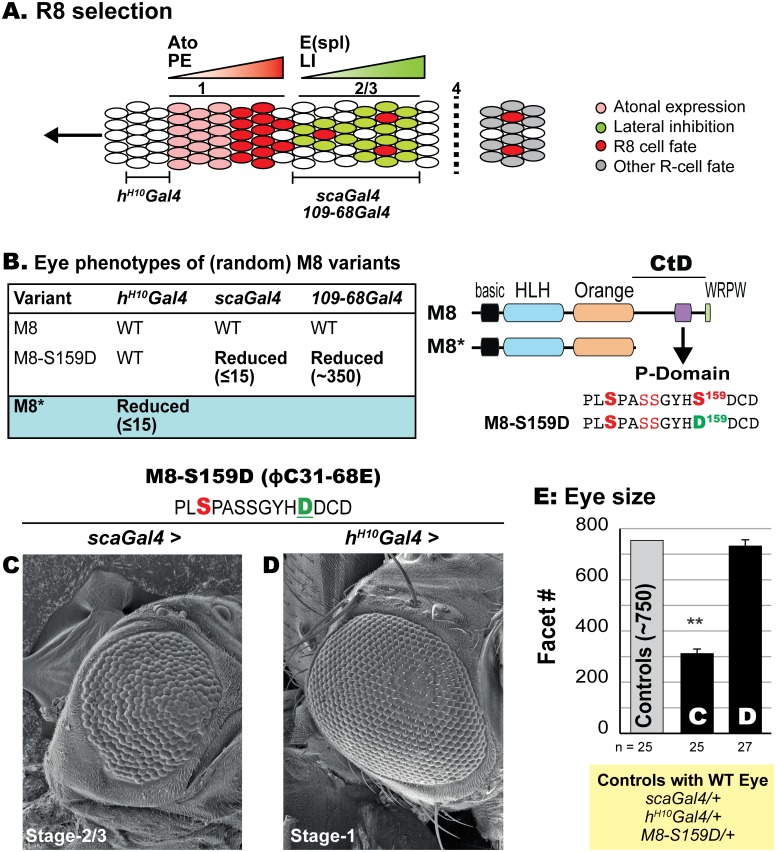
Fig 1. R8 selection and MF specificity of the CK2 mimic M8-S159D.
(A) Cell fate acquisition at different stages of the MF. Ato expression is upregulated in response to proneural enhancement (PE), which is followed by lateral inhibition (LI) through the E(spl) repressors. Color codes of cell fates is shown in inset, and expression domains of Gal4 drivers used in the studies are indicated relative to stages of the MF; the vertical dashed line denotes sequential recruitment of secondary photoreceptors. (B) The reduced eye phenotype of CK2 variants (random insertions) or M8*, the product of the E(Spl)D allele, upon expression at stage-1 (hH10Gal4) and at stage-2/3 (scaGal4 and 109-68Gal4). The reduced eye is denoted by number of ommatidia (facets) remaining; WT denotes facet counts between 750–800 and no perturbation of the hexagonal architecture of the adult eye. Note that the reduced eye of M8-S159D only manifests at stage-2/3, whereas that of M8* occurs at stage-1. Schematic to the right of panel B depicts the domains of E(spl)-M8 and CtD deletion in M8*, and sequence of the P-domain highlighting the CK2 site (S159DCD) that was altered to generate the CK2 mimic M8-S159D. The domains are indicated and include a C-terminal WRPW motif (Gro-binding). (C, D) Scanning EM of the adult eye at 200x. Overexpression of the CK2 mimic M8-S159D elicits a reduced eye at stage-2/3 of the MF (C), but not at stage-1 (D). (E) For each genotype, the number of images analyzed for eye size (ommatidial/facet counts) is indicated. Genotypes shown in panels C and D were compared to controls, and ** denotes P-value < 0.001.