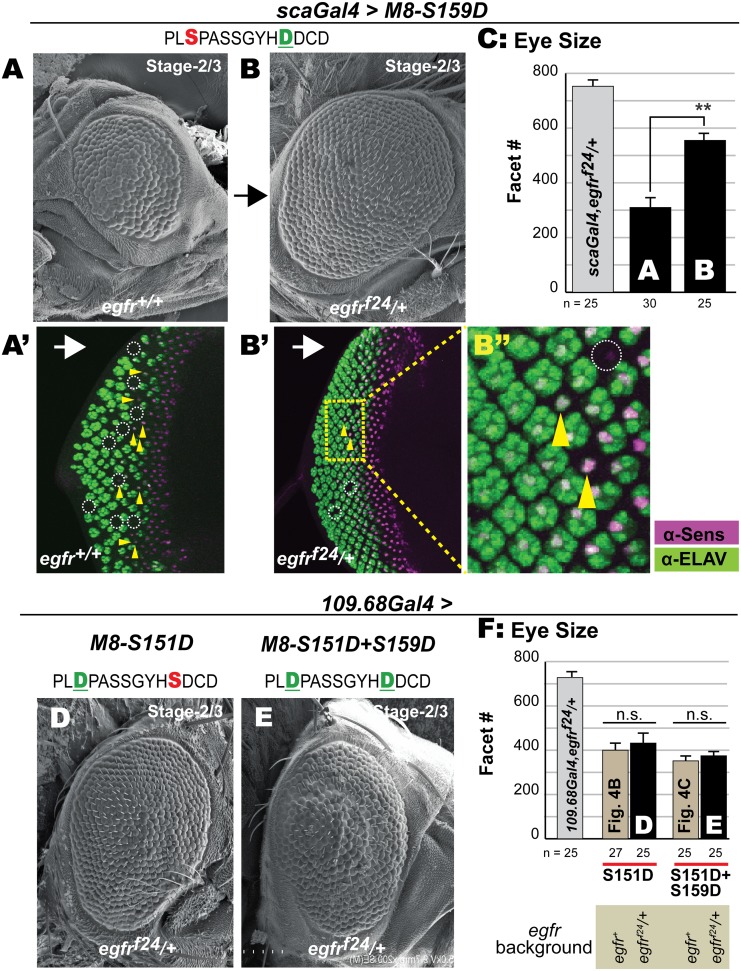
Fig 7. Halved egfr dosage mitigates the reduced eye of the CK2 mimic, but not the MAPK mimics.
(A-B) Scanning EM of adult eye at 200x magnification. The reduced eye of the CK2 mimic M8-S159D at stage-2/3 (A) is significantly attenuated (rescued) in the egfrf24/+ background (B). (C) Graph showing eye size; histograms labeled A and B correspond to the eyes in panels A and B. For each genotype, the number of images analyzed for eye size (ommatidial/facet counts) is indicated. Values for genotype shown in panel B were compared to that in panel A (the relevant control) and ** denote P-value < 0.001. Eye size in scaGal4/+; egfrf24/+ flies was not the control and included to illustrate a WT-eye in this genetic background. (A’-B’) Eye discs of genotypes in A and B were stained to label differentiated R8s (α-Sens) and secondary photoreceptors (α-ELAV). Arrows indicate direction of MF, dotted circles denote missing R8s and secondary photoreceptors, and arrowheads denote recruitment defective R8s. Panel (B”) shows a magnified image of (dashed) yellow box in B’ to highlight rescue of Sens+Elav clusters, although a few R8s fail to recruit Elav+ cells. In contrast, the reduced eye of the MAPK mimic M8-S151D (D) and the dual kinase (CK2+MAPK) mimic M8-S151D+S159D (E) are not rescued in the egfrf24/+ background. (F) For each genotype, the number of images analyzed for eye size (ommatidial/facet counts) is indicated. Genotypes shown in panels D and E were compared to their corresponding controls, i.e., values from Fig 4B and 4C, respectively, (‘n.s.’ denotes not significant). Eye size in 109-68Gal4/+; egfrf24/+ flies was not the control and included to illustrate a WT-eye in this genetic background.