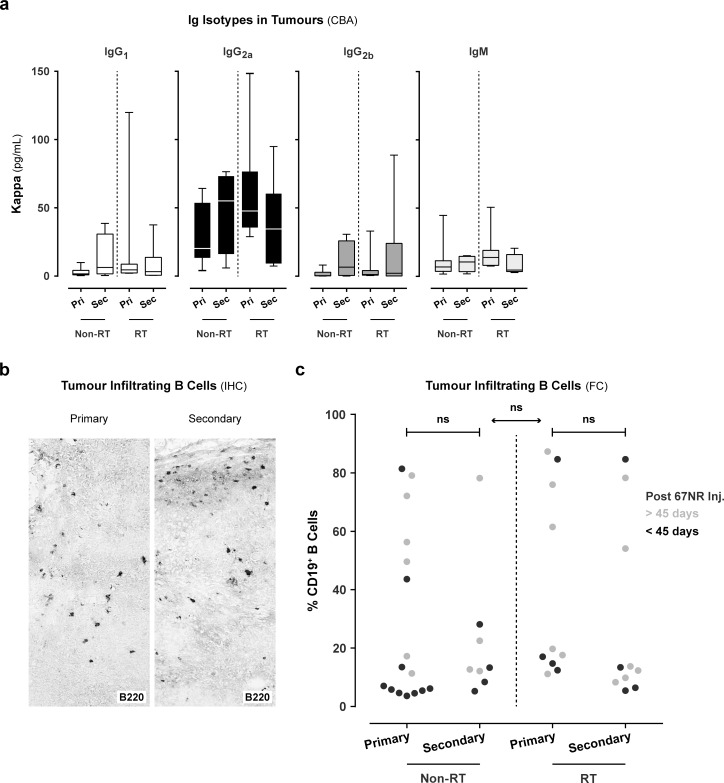
Fig 5. Infiltration of immunoglobulins and B cells in the primary and secondary tumour.
a. To determine the quantity of immunoglobulin (Ig) isotypes (IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgM) in both tumours, we used a cytometric bead assay (CBA). The isotype quantity was determined using a standard curve per isotype. These values were corrected for total protein content of the tumour lysates and displayed as μg/mL for isotypes kappa IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgM. b. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of tumour infiltrating B cells (B220) in the primary and secondary tumour (data representative for all animals). c. Detection of B cells in the primary and secondary tumours using flow cytometry (FC). Gating strategy: Living haematopoietic cells (CD45+ vs. 7-AAD-) were gated. In this gate, the lymphocyte population was selected based on the forward- (FSC) vs. sideward (SSC) scatter. To ensure that only lymphocytes were gated, CD11c+ cells were excluded. The CD19+ B cells were selected in the CD11c- gate. The percentage CD19+ B cells in the primary and secondary tumour of (non)- vs. irradiated animals (black or grey, respectively < 45 or > 45 days after 67NR tumour inoculation). Mann-Whitney t-test.