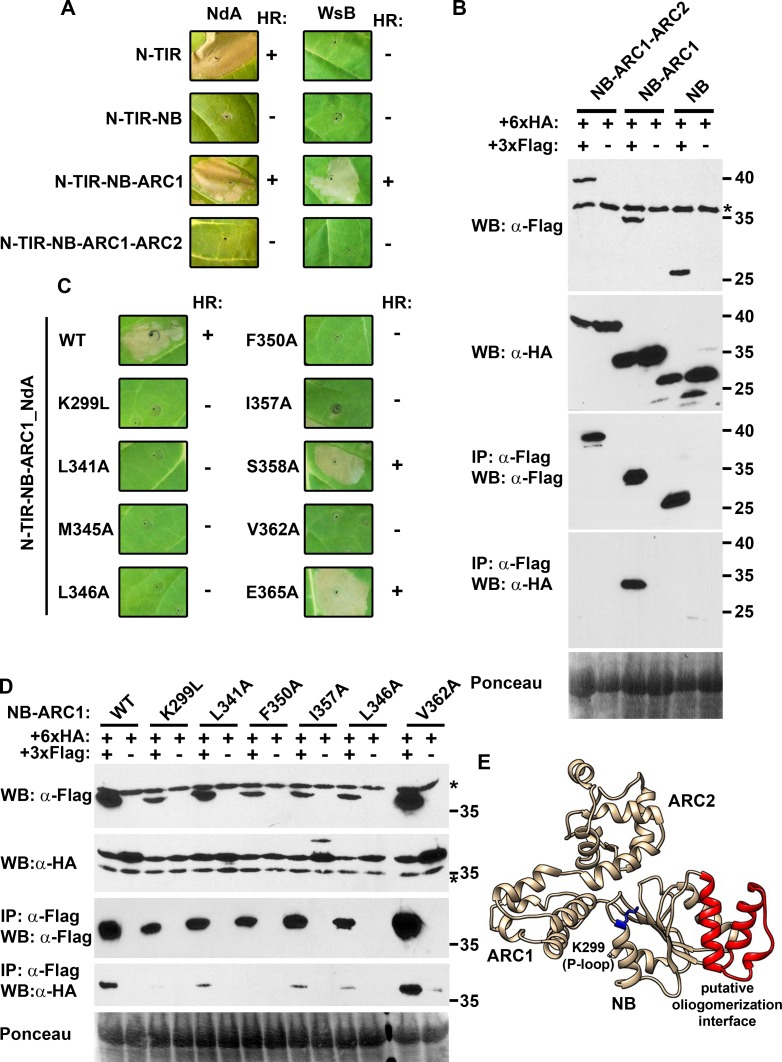
Fig 3. The NB-ARC domain influences N-TIR domain autoactivity.
(A) Hypersensitive response (HR) phenotypes are altered by the successive addition of NB, ARC1, and ARC2 subdomains to the N-TIR domains of the RPP1 alleles Niederzenz (NdA) or Wassilewskija (WsB). Constructs were tested in Nicotiana tabacum via Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression and images were captured at 48 hours post-infiltration (hpi). The presence or absence of HR is indicated by a “+” or “-“, respectively. (B) Detection of self-association between NdA NB-ARC subdomain truncations by co-immunoprecipitation. Differentially epitope-tagged versions of NB, NB-ARC1, or NB-ARC1-ARC2 proteins were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana and samples were collected at 48 hpi for co-immunoprecipitation using α-Flag agarose beads. Asterisks indicate non-specific bands. Staining of RuBisCO with Ponceau S provides a loading control. (C) Site-directed mutagenesis of the NB subdomain compromises HR induction in an NdA N-TIR-NB-ARC1 background. Constructs were tested as in (A); protein expression for constructs from (A) and (C) is documented in S9 Fig. (D) Detection of self-association of NB-ARC1 mutants by co-immunoprecipitation, tested as in (B). Experiments were performed at least three times with similar results. (E) Predicted structure of the RPP1 NB-ARC domain derived from homology modeling using the Drosophila Dark protein (PDB:4v4l) as a template. The K299 residue within the P-loop is denoted in blue, while the putative oligomerization interface is highlighted in red. The specific residues at the putative oligomerization interface that were analyzed by mutagenesis are depicted in S10 Fig.