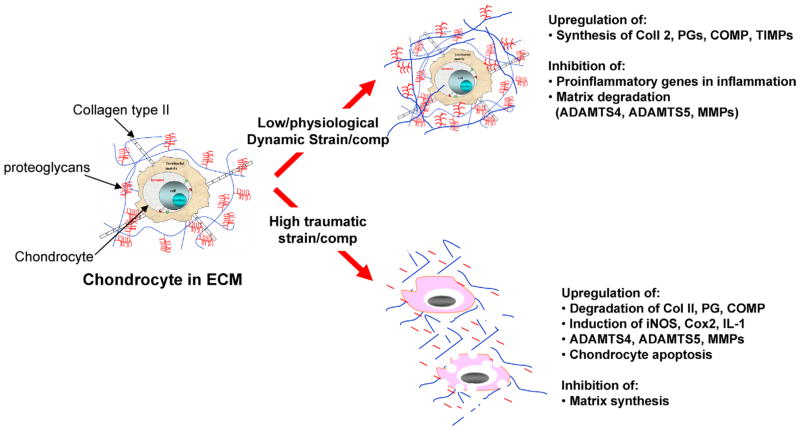
Fig. 2.
Transcriptional regulation of various genes in response to mechanical forces. Cyclic/dynamic compressive and tensile forces of low magnitudes upregulate synthesis of matrix associated proteins such as proteoglycans, collagen type II, aggrecan, TIMPs and COMP. In addition, biomechanical signals of low magnitudes inhibit IL-1β-induced expression of proinflammatory genes as well as abrogate cytokine mediated inhibition of synthesis of matrix associated proteins. Contrarily, dynamic/static compressive and tensile forces of high magnitudes and static forces induce expression of proinflammatory genes that are associated with matrix destruction such as iNOS, COX-2, MMPs, ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5. In parallel, these forces inhibit expression of matrix associated molecules such as aggrecan, collagen type II, TIMPs and COMP.