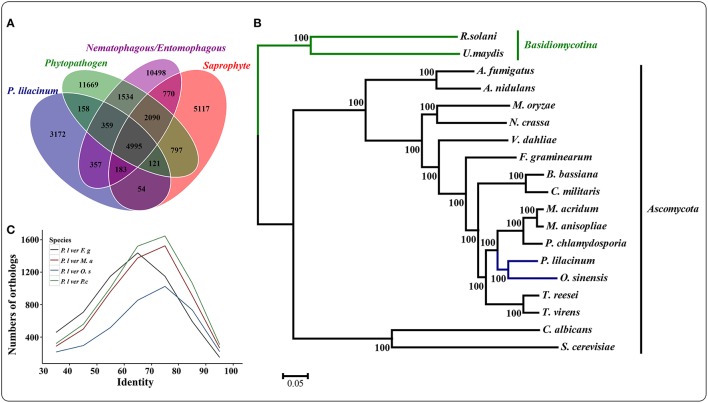
Figure 1.
Comparative genomics and evolutionary analysis of P. lilacinum strain 36-1. (A) Numbers of homologous families between different fungi with different lifestyle. Phytopathogenic fungi include Fusarium graminearum, Magnaporthe oryzae, and Ustilaginoidea virens; Saprophytism include Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, and Aspergillus nidulans. Nematophagous/Entomophagous fungi include Ophiocordyceps sinensis, Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium acridum, Cordyceps militaris, and Pochonia chlamydosporia; (B) A maximum likelihood phylogenomic tree constructed using the Dayhoff amino acid substitution model showing the evolutionary relationship of P. lilacinum strain 36-1 with other fungi; (C) Numbers of orthologous genes with different levels of protein identity between P. lilacinum strain 36-1 and other fungi. Identity refers to the reciprocal similarity (>30%) of proteins between P. lilacinum and other fungi by BLASTP.