Figure 4.
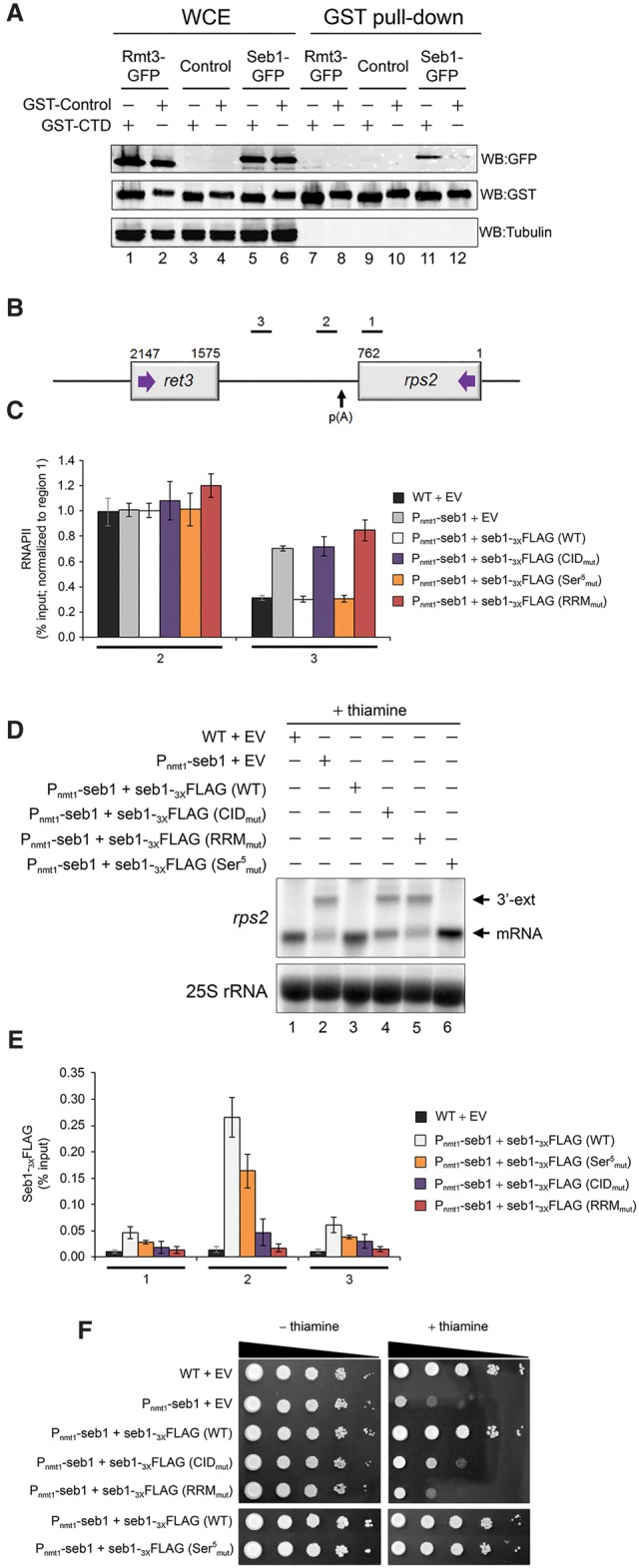
Seb1 requires functional CID and RRM domains for accurate 3′ end processing and transcription termination. (A) Immunoblot analysis of whole-cell extracts (WCE) (lanes 1–6) and glutathione-sepharose pull-downs (lanes 7–12) prepared from the indicated strains expressing either GST-CTD (odd-numbered lanes) or a control GST fusion protein (even-numbered lanes). (B) Bars above the rps2 gene show the positions of PCR products used for ChIP analyses. (C) RNAPII ChIP analysis using extracts prepared from the Pnmt1-seb1 conditional strain containing genomically integrated constructs that express the indicated versions of Flag-tagged Seb1 (wild type, CIDmut, Ser5mut, and RRMmut) (see the text; Supplemental Fig. S5a for description) as well as an empty control vector (EV). Cells were grown in the presence of thiamine to deplete endogenous Seb1. Error bars indicate SD. n = 3 biological replicates from independent cell cultures. (D) Northern blot analysis of rps2 mRNA from the indicated strains. The rps2 3′ extended transcripts are shown (3′-ext). (E) ChIP analyses of wild-type and mutant versions of Seb1-Flag along the rps2 gene. Control wild-type cells with an empty vector (black bars) were used as a negative control for the anti-Flag ChIP assays. Error bars indicate SD. n = 3 biological replicates from independent cell cultures. (F) Tenfold serial dilutions of the indicated strains were spotted on thiamine-free (left) or thiamine-containing (right) minimal medium.
