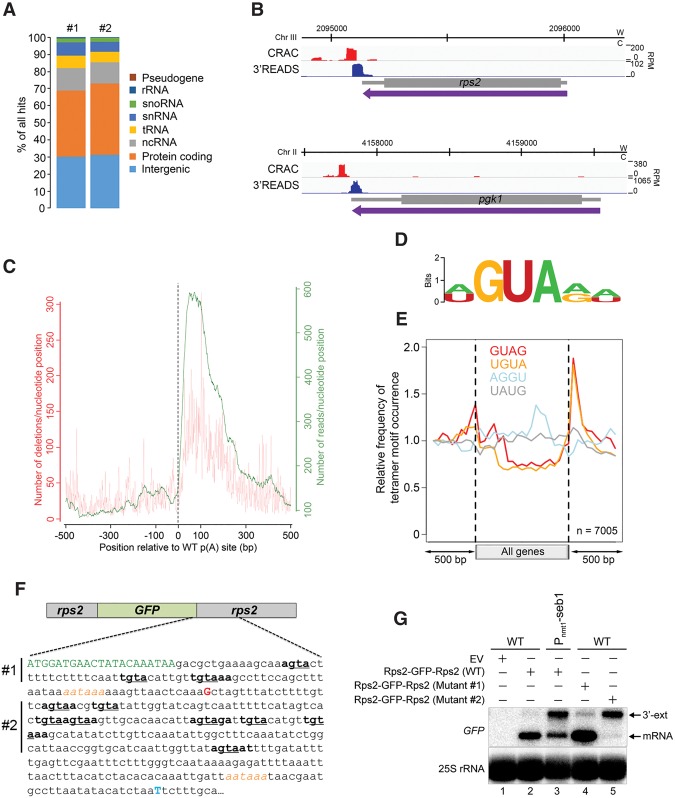
Figure 5.
Seb1 binds to GUA-containing motifs downstream from poly(A) sites. (A) Distribution of Seb1-bound reads between transcript classes for two independent CRAC experiments. (B) Seb1 CRAC cDNA read distribution (red) and 3'READS profile (blue) of rps2 and pgk1 genes in a wild-type strain. (W) Watson strand; (C) Crick strand; (RPM) reads per million. (C) Cumulative Seb1 RNA-binding sites relative to annotated poly(A) sites. The green curve (right Y-axis) shows the number of reads per nucleotide position, which is a measure of the binding preference. The red curve (left Y-axis) shows the number of deletions per nucleotide position, which is an indication of direct cross-linking. (D) Sequence logo of Seb1 cross-linking sites derived from the WebLogo application (Crooks et al. 2004) using the top 10 pyMotif-derived k-mers from each CRAC experiment. (E) Average gene distribution of tetrameric motifs derived from the Seb1 CRAC data (GUAG and UGUA) and control tetramers with shuffled dinucleotides (AGGU and UAUG). (F) Schematic of the rps2-GFP-rps2 construct used to address the functional significance of the Seb1 consensus motif in poly(A) site selection. Shown is a 405-nt region that includes the last seven codons of the GFP mRNA (in green) as well as the major poly(A) site of the GFP-rps2 mRNA detected in wild-type (G shown in red; +89 from stop codon) and Seb1-depleted (T shown in blue; +376 from stop codon) cells, as determined by 3′ RACE. The AAUAAA poly(A) signals are italicized in orange. Sequences in bold show Seb1 consensus motifs with the GUA core underlined. In mutant #1, the GUA core of the three Seb1 binding motifs located upstream of the wild-type rps2 cleavage site was mutated to CAC, whereas mutant #2 introduced CAC mutations in the eight Seb1-binding motifs located downstream from the rps2 cleavage site. (G) Northern blot analysis using total RNA prepared from wild-type (lanes 1,2,4,5) and Seb1-deficient (lane 3) cells that express either wild-type (lanes 2,3) or mutant (mutant #1 [lane 4] and mutant #2 [lane 5]) versions of the GFP-rps2 construct. Cells were grown in the presence of thiamine. The blot was analyzed using probes specific for the GFP mRNA and 25S rRNA.