Figure 1.
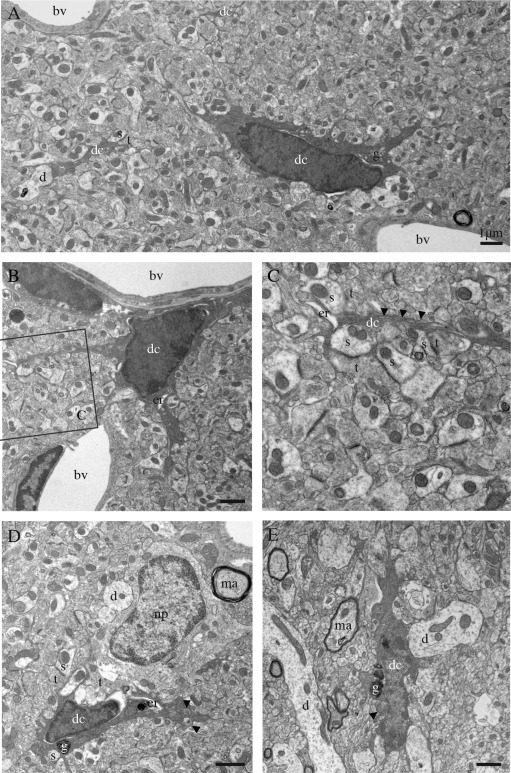
Ultrastructural features of the dark microglia. A–E: Examples of dark microglial cells (dc) encountered in the CA1 region of the hippocampus (stratum lacunosum‐moleculare) of stressed CX3CR1 knockout mice (A–D) or in the median eminence of the hypothalamus in a nontransgenic control mouse (E). In addition to their ultrastructural features of microglia, for instance their frequent long stretches of endoplasmic reticulum (arrowheads in C), these cells are recognized by their various signs of oxidative stress: their condensed, electron‐dense cytoplasm and nucleoplasm, accompanied by cytoplasmic shrinkage, Golgi apparatus (g) and endoplasmic reticulum (er) dilation, and mitochondrial alteration (arrowheads in D, E). Examples of endoplasmic reticulum dilation in cell bodies and a process are, respectively, provided in (B), (D), and (C). The dark microglia contain lipofuscin granules (g) in (D) and (E). Direct contacts with blood vessels (bv), dendrites (d), a neuronal perikaryon (np), axon terminals (t) and dendritic spines (s), and synapses between axon terminals and dendritic spines are also shown. ma = myelinated axon. Scale bars = 1 μm.
