Figure 6.
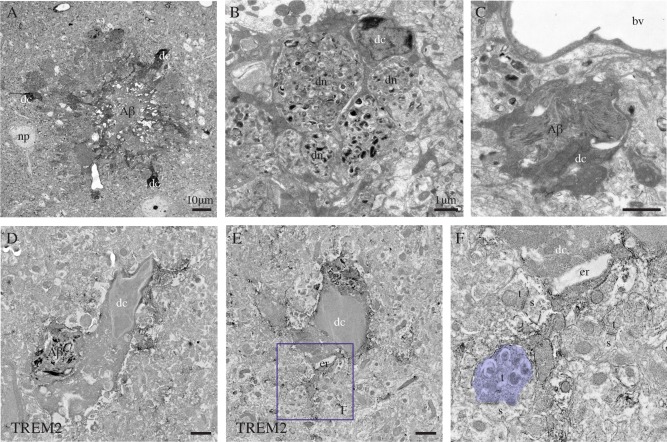
Dark microglia's association with the plaques of amyloid β, examples from the prefrontal cortex subgranular layers (A–C) and CA1 lacunosum‐moleculare (D–F) of 6‐ and 21‐month‐old APP‐PS1 mice, respectively. In (A), three dark microglial cells (dc) showing several signs of cellular stress (i.e., extreme condensation, darkening of their cytoplasm and nucleoplasm) are observed in the close proximity of a plaque of amyloid β (Αβ), which is identified by its ultrastructural features. In (B), farther from the plaque, a dark microglial cell process is encircling several dystrophic neurites (dn) containing autophagic vacuoles. In (C) and (D), a dark cell body (D) and process (C) are containing Αβ deposits. D–F: Examples of dark microglial cells that exhibit immunostaining for TREM2, as frequently observed nearby the plaques of Αβ. The remodeling of their nuclear contents can be noted in D and E, together with the pronounced dilation of their endoplasmic reticulum (er) in (E). In addition, the dark microglial cell in (E) is contacting an axon terminal (colored in purple, t) with an accumulation of autophagic vacuoles that makes a synapse on a healthy looking dendritic spine (s). bv = blood vessel and np = neuronal perikaryon. Scale bars = 10 μm for (A), and 1 μm for (B–E). [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
