Figure 2.
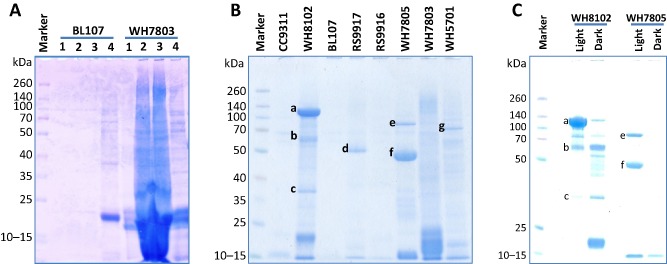
Exoproteomes of different marine S ynechococcus strains. Concentrated exoproteomes equivalent to 40 ml of culture were resolved by 10% Tris‐Bis NuPAGE gel (Invitrogen) and stained with coomassie G‐250 (SimplyBlue SafeStain, Invitrogen). Spectra Multicolor Broad Range Protein Ladder (Fermentas) was used as a marker. (A) Process for optimizing exoproteome preparation. The exoproteomes from S ynechococcus spp. BL107 and WH7803 were prepared from cultures: lane 1, washed cells in fresh ASW (107 cells ml−1) and incubated for 2 days; lane 2, routinely subbed cultures (15% volume from an older culture in fresh ASW medium, resulting in 107 cells ml−1) incubated for 2 days; lane 3, washed cells in fresh ASW (107 cells ml−1) and incubated for 14 days; lane 4, protein extract of the cellular fraction from the corresponding S ynechococcus strain. (B) Exoproteomes from each one of the eight S ynechococcus strains analysed in this study by shotgun proteomics. Preparation of the exoproteomes was as indicated in the section E xperimental procedures. Letters indicate those resolved protein bands that were further identified using chymotrypsin digestion prior to LC‐MS‐MS: (a) SwmA NP_896180.1; (b) SwmA NP_896180.1 and SwmB NP_897046.1; (c) substrate binding protein of a phosphate ABC transporter NP_897111.1; (d) chitinase ZP_01081204.1; (e) type I secretion protein EAR18050.1; (f) haemolysin EAR19380.1 and chitinase EAR19694.1; (g) alkaline phosphatase EAQ75607.1. (C) Exoproteomes from light/dark incubated cultures of S ynechococcus sp. WH8102 and WH7805. Bands a, b, c, e and f are as those highlighted in panel B.
