Figure 3.
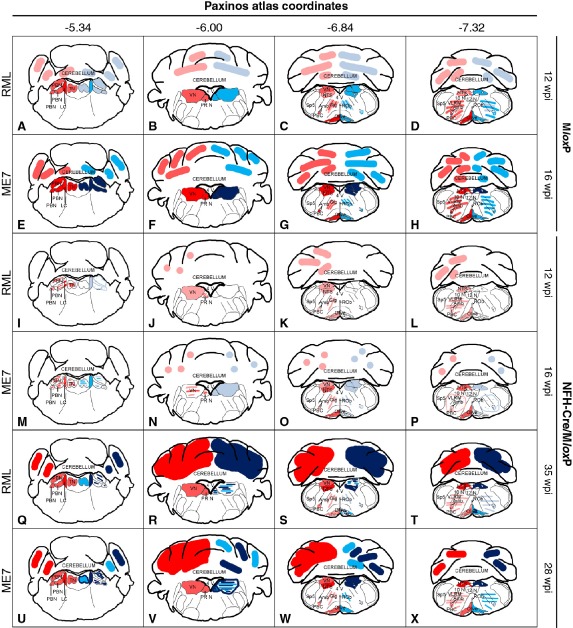
Progression of prion pathology in RML‐ and ME7‐inoculated MloxP and NFH‐Cre/MloxP mice. Schematic drawings of abnormal PrP deposition (pink = mild, red = intermediate, dark red = severe) and spongiosis (pale blue = mild, blue = intermediate, dark blue = severe) of the brainstem nuclei analysed, at four representative levels from coordinates −5.34 mm to −7.64 mm caudal from bregma. The inoculum is shown on the left margin. Genotype and incubation times on the right margin. (A–D) In terminally ill RML‐inoculated MloxP mice (12 wpi) PrP deposition is seen in different areas of the brainstem, including the locus coeruleus and the olive; prepositus nuclei and tegmental nuclei; and pre‐Bötzinger complex; spongiosis corresponds to PrP deposition in most areas. (E–H) In terminally ill ME7 inoculated MloxP mice (16 wpi), abnormal PrP deposition was severe in all the nuclei examined, except the gigantocellular nucleus, the ventral medulla and the cerebellum, where it was intermediate. Spongiosis pattern corresponds to PrP deposition in most areas. (I–L) RML‐inoculated NFH‐Cre/MloxP mice show a significantly lower overall accumulation at 12 wpi, and spongiosis was nearly absent everywhere, except for the locus coeruleus, where it was mild (pale blue). (M–P) In ME7‐inoculated NFH‐Cre/MloxP mice culled at 16 wpi, abnormal PrP accumulation was slightly stronger than in RML‐inoculated animals and more heterogeneous. Spongiosis was reduced everywhere compared with ME7‐inoculated MloxP mice at end stage of prion disease. Strong PrP deposition and spongiosis was observed in terminally ill RML‐inoculated NFH‐Cre/MloxP mice (35 wpi, Q–T), or in terminally ill ME7‐inoculated NFH‐Cre/MloxP mice (28 wpi) (U –X). 10 N, nucleus of the X nerve; 12 N, nucleus of the XII nerve; 4 V, forth ventricle; Amb, nucleus ambiguous; LC, locus coeruleus; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; PBC, pre‐Bötzinger complex; PBN, parabrachial nuclei; PR N, prepositus nucleus; ROb, raphe obscurus; Sp5, Spinal nucleus of the V nerve; TN, tegmental nuclei; VLRM, ventro‐lateral reticular medulla; VN, vestibular nuclei; VN, vestibular nuclei.
