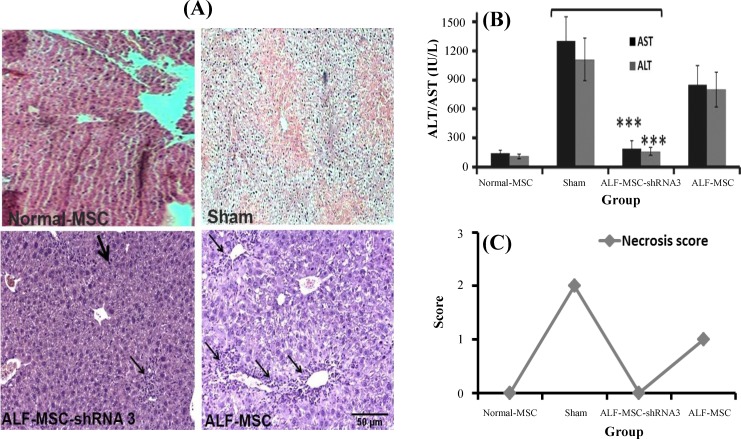
Fig. 4.
Therapeutic effects of different mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in acute liver failure (ALF)-induced mice 72 h after cell therapy. Normal MSCs and autophagy-modulated MSCs were transplanted in ALF-induced and normal mice that received normal MSCs were considered as control. Their therapeutic potentialities were evaluated after 72 h. (A) Histo/histopathological assay. A decreased number of inflammatory cells (narrow arrows) and the presence of repaired cells (thick arrow) were observed in ALF-MSC-shRNA 3. ALF-MSC (received MSCs without any manipulation) revealed increased inflammation and mild necrosis. Necrosis was observed in sham group (H&E stain, magnification 100×, scale bar: 500 µm). (B) Biochemical assay. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels approximately returned to the normal level in ALF-shRNA 3 compared with sham (mean±SD, ***P≤0.01). There was no significant difference between ALT and AST of ALF-MSC and sham. (C) Necrosis score quantification. Necrosis score was zero in MSC-shRNA 3 but the score was one in ALF-MSC and two in the sham group