Figure 2.
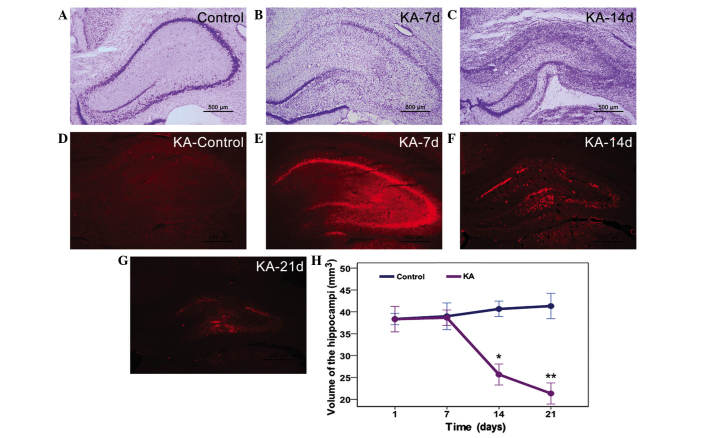
Neuronal albumin uptake correlates with neuronal injury, as detected by (A-C) Nissl staining and (D-G) Evans blue staining. Rats in the control group exhibited (A) normal hippocampal structure and (D) non-significant albumin leakage. (B) On the 7th day post-KA injection, Nissl staining demonstrated significant neuronal damage in the hippocampus around the KA injection site, (E) which was consistent with the distribution of albumin extravasation on the 7th day in the KA group. On the (C and F) 14th and (G) 21st days following KA injection, the hippocampi of rats in the KA group exhibited severe atrophy with significant loss of lesion volume and (F) albumin-positive cells, as compared with the (D) control and (E) KA-7 day group. (F and G) Minimal albumin-positive neurons were detected in the atrophied hippocampi. (H) Quantitative analysis showed a similar result. Scale bar, 500 µm. *P<0.001 and **P=0.12 vs. the control group. KA, kainic acid.