Figure 1.
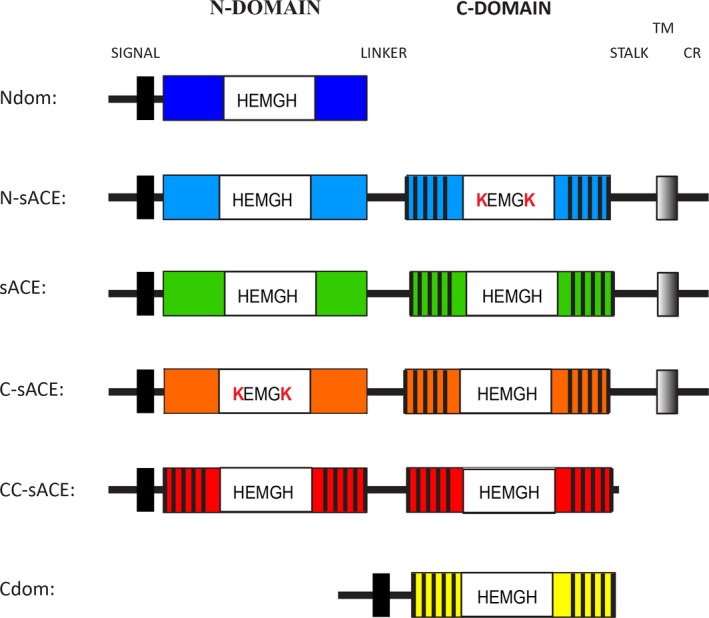
Schematic of the ACE constructs used. The wild‐type ACE (sACE) contains a signal peptide (black box), the two homologous ectodomains (C‐domain is indicated with black stripes) with the indicated active site residues necessary for the coordination of Zn, a stalk region, transmembrane domain (grey shaded box) and cytoplasmic region (CR). The truncated Ndom (dark blue) contains the signal peptide and the N‐domain. The truncated Cdom (yellow) is essentially the same as the C‐domain in wild‐type sACE only it lacks the transmembrane region and has the added signal peptide. The domain inactivated mutants are identical to sACE except for the mutation of the catalytic His residues to Lys (white boxes) in the N‐domain (N‐sACE) (blue) and C‐domain (C‐sACE) (orange). The CC‐sACE (red) construct is a fusion construct of two tandem copies of C‐domain.
