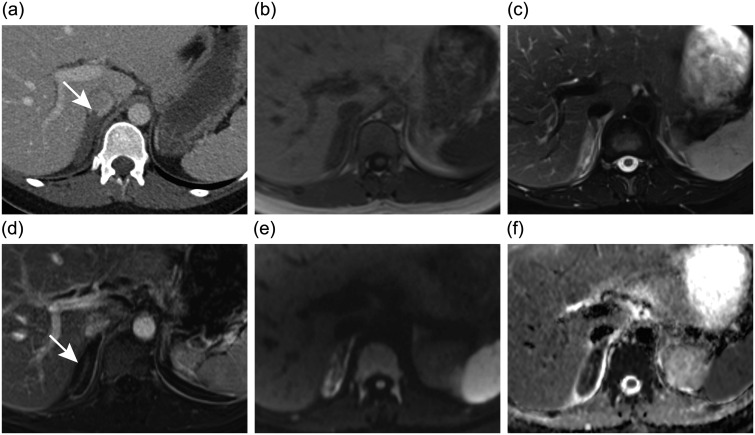
Figure 1.
Axial images at the level of the right adrenal gland. (a) Contrast-enhanced computed tomography image shows enlarged right adrenal gland and mild inflammatory changes in the adjacent fat. The tail of the adrenal vein thrombus (arrow) extending into the inferior vena cava can be seen. (b) T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) image shows no sign of adrenal haemorrhage. (c) T2-weighted fat-saturated MR image shows oedema of the right adrenal gland and adjacent fat. The adrenal vein thrombus is also seen. (d) Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted subtraction MR image shows capsular but no parenchymal enhancement of the right adrenal gland (arrow). (e and f) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging and the corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient map demonstrate restricted diffusion of the right adrenal gland consistent with infarction.