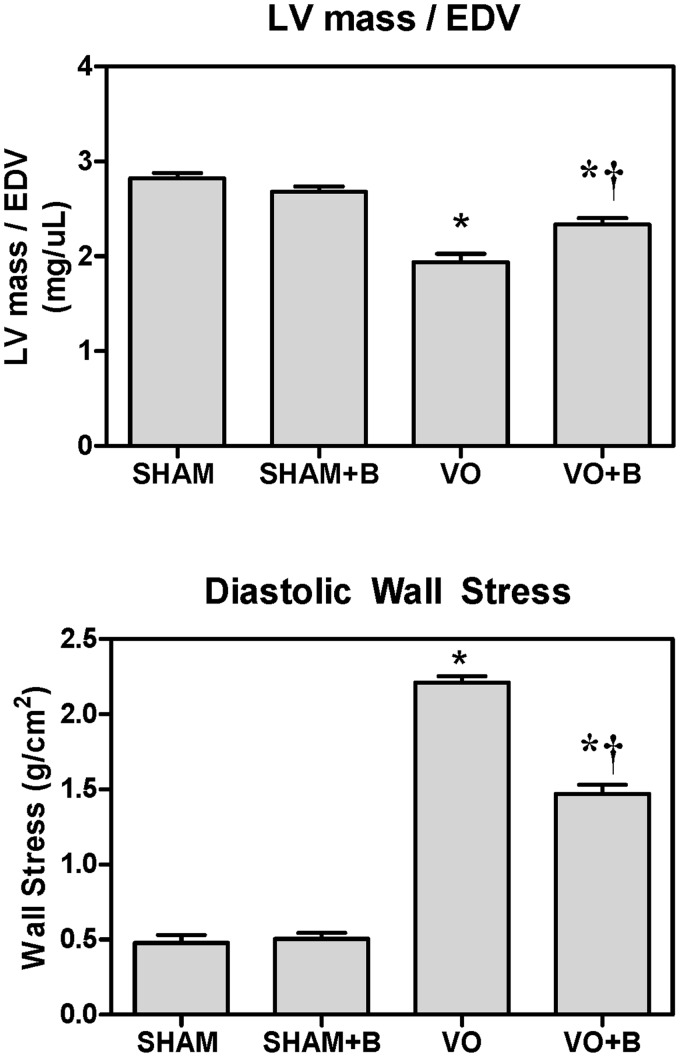
Figure 2.
Lysyl oxidase (LOX) inhibition attenuated volume overload (VO)-induced increases in cardiac wall stress. TOP: A ratio between left ventricular (LV) mass and end diastolic volume (EDV) was calculated to assess cardiac stress. LV mass was determined from wet weight and LV EDV was determined by pressure–volume catheterization. The ratio decreased in VO, indicative of increased cardiac stress. LOX inhibition with beta-aminoproprionitrile (BAPN;B) attenuated these decreases. Similar results and statistical significance were obtained using LV mass and volume estimated by echocardiography (data not shown). BOTTOM: A calculation of diastolic stress using Equation 1 confirms that LOX inhibition attenuated VO-induced increases in cardiac stress. Statistical significance denoted as P < 0.05 vs. Sham (*) and VO (†); n = 4–8 per group