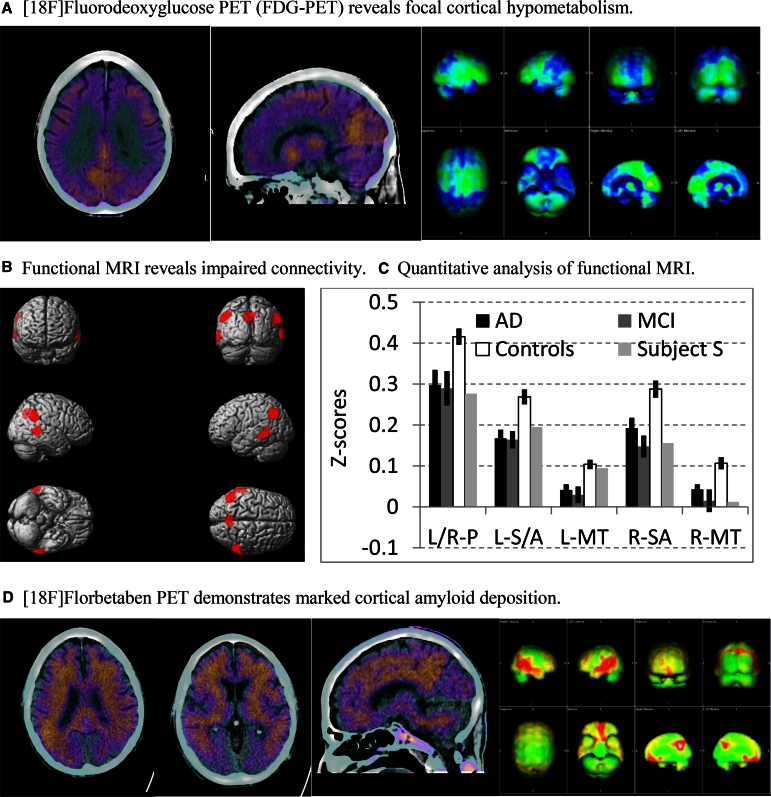
Fig. 1.
(A) The two fused FDG-PET/CT images on the left demonstrate reduced activity in the bilateral parietal cortex and posterior cingulate/precuneus. The panel on the right shows projection maps (Syngo.via software, Siemens Medical Solutions, PA, USA) with areas of reduced activity in the temporoparietal regions and precuneus bilaterally. A voxel-based analysis was conducted with comparison to a normal age-matched database. Regions at least 3 SDs below the normal reference value were considered abnormal and displayed in blue. Specifically, these brain regions (with corresponding SDs below the normal reference value) were L parietal (6.5), R parietal (4.5), L frontal (3.9), and L temporal (3.1). (B) Functional MRI (fMRI). Six minutes of resting state fMRI data were collected from 22 HIV-uninfected individuals with mild cognitive impairment (mild cognitive impairment [MCI]; n = 8) or mild AD (n = 14; age 69.4 ± 7.5, 13 males) and 42 age-matched cognitively normal controls (age 67.4 ± 5.1, 14 males). Standard fMRI preprocessing procedures were followed [12]. After regressing out nuisance factors including head movements, global signal variations, and signal in white matter and CSF, we used the posterior cingulate cortex (PPC; left and right collapsed together) as the seed region, and obtained the correlation coefficients between PPC and other brain regions. The correlation coefficients were then z-transformed and entered into second-level whole brain analysis. The contrast of controls >MCI/AD revealed decreased connectivity between PPC and left and right precuneus, left and right supramarginal/angular gyrus, and left and right middle temporal region (threshold, P < .005 uncorrected, at least 200 contiguous voxels). (C) The mean Z-scores for the connectivity between PPC and the regions of interest (ROIs) identified in (B) from HIV-uninfected individuals with mild AD or MCI, controls, and the subject (Subject S). The profile of resting state connectivity in this subject is similar to HIV-uninfected individuals with MCI or mild AD. Error bars represent SEM. L/R-P, left/right precuneus; L-SA, left supramarginal/angular gyrus; R-SA, right supramarginal/angular gyrus; L-MT, left middle temporal region; R-MT, right middle temporal region. (D) The three images on the left show areas of at least moderate amyloid deposition in the frontal, parietal, temporal regions, and posterior cingulate/precuneus. The panel on the right shows projection maps (Syngo.via software; Siemens Medical Solutions, USA) with areas of increased amyloid deposition (shown in red). A visual and ratio analysis was conducted using the cerebellar cortex as reference. The SUVr is the ratio of the individual standardized uptake value (SUV) for each of the brain regions compared with the SUV of the cerebellar cortex. Specifically, the SUVr values were as follows: posterior cingulate 1.99, parietal 1.95, temporal 1.89, frontal 1.81, anterior cingulate 1.6, occipital 1.53, average 1.8. FDG, [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose; SD, standard deviation; AD, Alzheimer's disease; SEM, standard error of the mean.