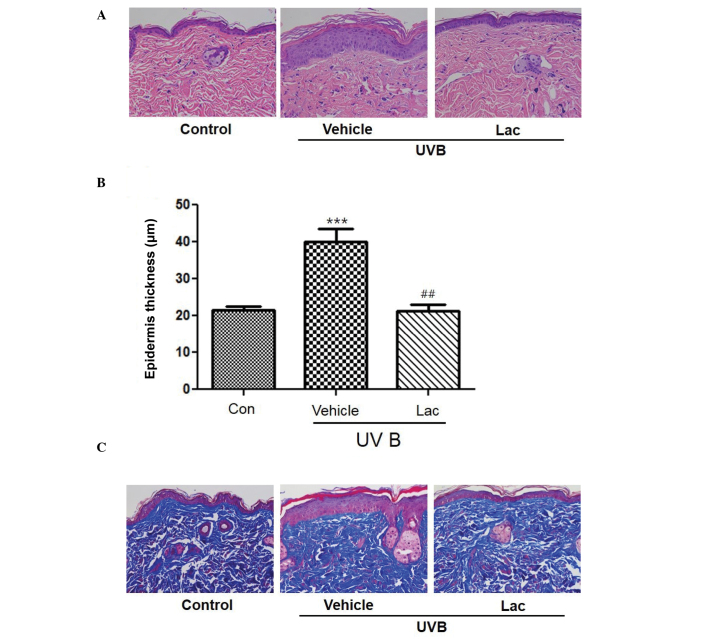
Figure 2.
Tyndalized Lactobacillus acidophilus treatment reduced UVB-induced skin thickening in hairless mice. (A) Tyndalized L. acidophilus suppressed the UVB-induced increase in epidermal thickness. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of UVB-irradiated hairless mice skin. Magnification, ×200. (B) Epidermal thickness of the dorsal skin. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error. ***P<0.001 vs. the control group. ##P<0.01 vs. the vehicle group. (C) Protective effect of tyndalized L. acidophilus against changes in the number of collagen fibers. Histological staining of hairless mouse skin stained with Masson's trichrome stain. Collagen fibers are stained blue. Magnification, ×200. Lac, tyndalized L acidophilus; UVB, ultraviolet B.