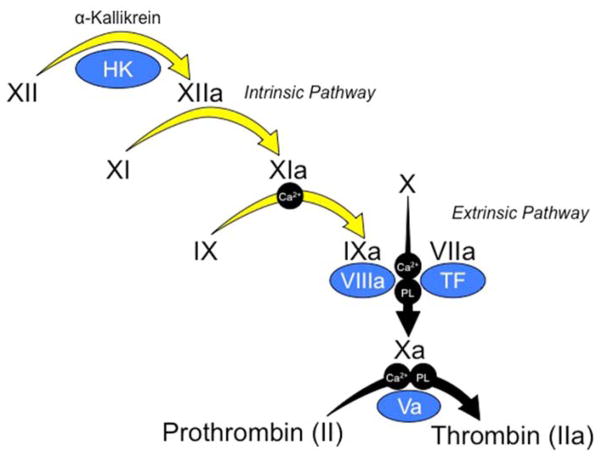
Figure 1. Traditional Cascade-Waterfall Model of Thrombin Generation.
Black Roman numerals indicate inactive zymogens of plasma proteases, and the lowercase “a” indicates active protease. Co-factors are indicated in blue ovals. Requirements in some reactions for calcium ions (Ca2+) and phospholipid (PL) are indicated. In the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT assay), coagulation is initiated by activation of fXII on a charged surface in a process called contact activation, which involves the protease α-kallikrein and the cofactor high molecular weight-kininogen (HK). FXIIa triggers converting of fXI to fXIa, and fXIa in turn converts fIX to fIXa. The series of reactions indicated by yellow arrows are referred to as the intrinsic pathway. The intrinsic pathway converts fX to fXa. FXa then cleaves prothrombin to generation thrombin. The intrinsic pathway can be bypassed by the extrinsic pathway, which is comprised of fVIIa in complex with the cofactor tissue factor (TF). Activation of fX through the extrinsic pathway is the basis of the prothrombin time (PT) assay.