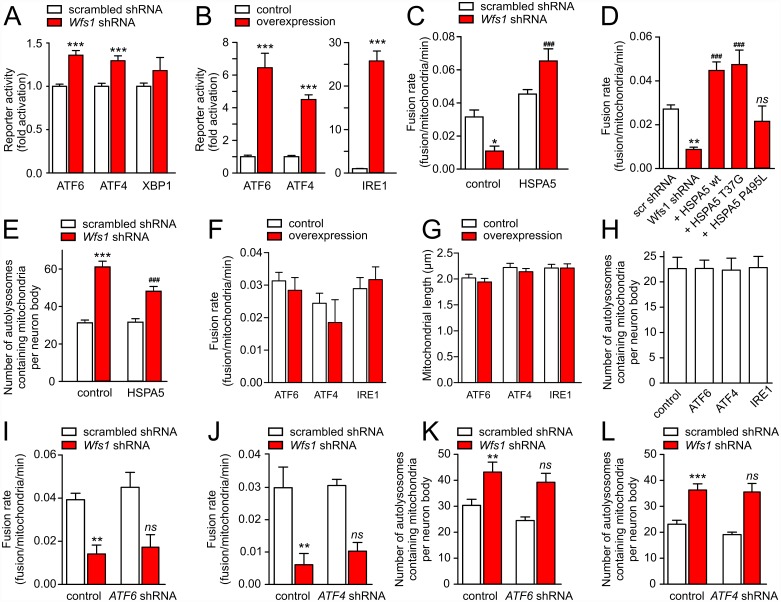
Fig 3. WFS1 deficiency induces mild ER stress in primary cortical neurons.
(A) Neurons were transfected with plasmids expressing scrambled shRNA or Wfs1 shRNA, firefly luciferase constructs containing ATF6 or ATF4 binding sites or a XBP-1 splicing reporter, and Renilla luciferase. Firefly luciferase signal normalized to Renilla signal demonstrates a moderate increase in ATF6 and ATF4 reporter activity. (B) Positive control experiments in which the above-mentioned reporter systems and Renilla luciferase were co-transfected with ATF4, ATF6, or IRE1. (C) The mitochondrial fusion rate is reduced by Wfs1 shRNA and is restored by co-expressing wt HSPA5 (p = 0.001 for interaction, two-way ANOVA). (D) ATPase-deficient HSPA5 mutant (T37G) but not peptide binding-deficient mutant (P495L) restores the fusion rate reduced by Wfs1 shRNA. (E) HSPA5 overexpression attenuates mitophagy activated by Wfs1 silencing (p = 0.012 for interaction). (F–H) Activation of the primary ER stress pathways by overexpression of ATF6, ATF4, or IRE1 modulates neither fusion rate (F), mitochondrial length (G), nor mitophagy (H). (I–L) Silencing of ATF6 or ATF4 modulates neither fusion rate (I, J) nor mitophagy (K, L). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared with respective control groups, or ###p < 0.001 compared with the Wfs1 shRNA-transfected control group and ns non-significant compared with the Wfs1 shRNA-transfected control group. Underlying data is shown in S1 Data.