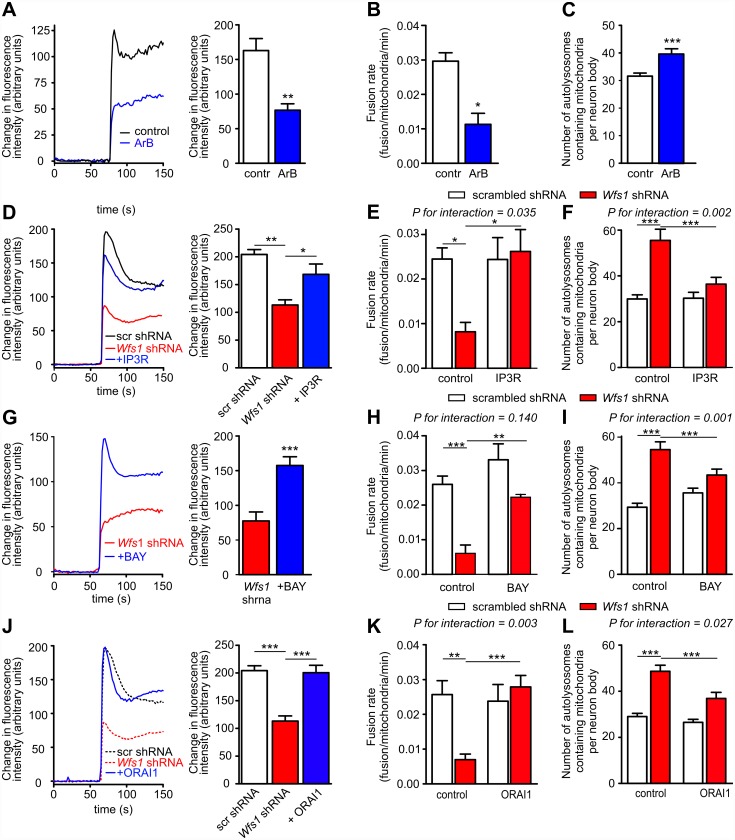
Fig 5. Cytosolic Ca2+ homeostasis regulates the mitochondrial fusion rate and mitophagy in primary cortical neurons.
(A–C) The IP3R inhibitor Araguspongin B (5 μM) decreases KCl-induced Ca2+ transients (A), reduces the mitochondrial fusion rate (B), and increases mitophagy in control neurons (C). For D–L, neurons were transfected with the mitochondrial marker mKate2-mito and scrambled shRNA (white bars) or Wfs1 shRNA (red bars). (D–F) Under conditions of WFS1 deficiency, IP3R overexpression restores the depressed cytosolic Ca2+ response to 25 mM KCl (D) and normalises the mitochondrial fusion rate (E) and mitophagy (F). (G–I) Similarly, under conditions of WFS1 deficiency, the L-type Ca2+ channel agonist Bay K 8644 (5 μM) increases the cytosolic Ca2+ response to KCl (G) and normalises the mitochondrial fusion rate (H) and mitophagy (I). (J–L) Overexpression of ORAI1 has similar effects (dotted lines in J represent responses of cells treated with scrambled or Wfs1 shRNAs already shown in D). *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 versus indicated groups. P-values for interactions are given in the figures. Underlying data is shown in S1 Data.