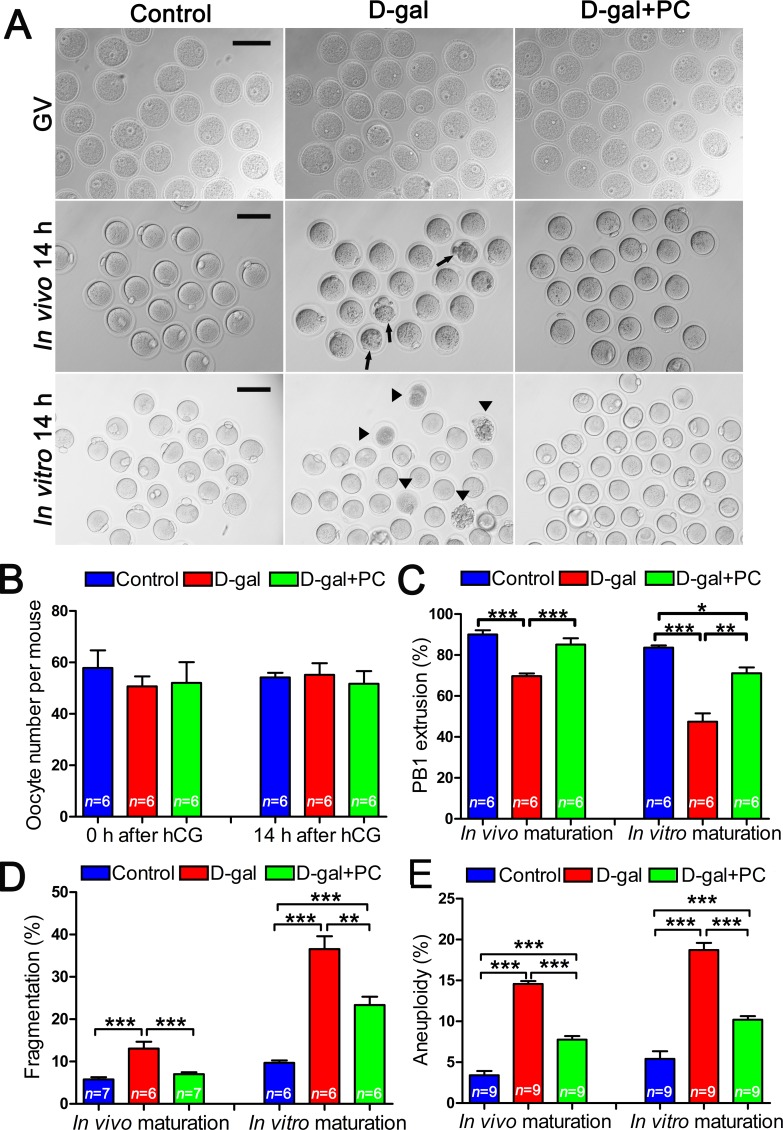
Figure 2. Impaired oocyte quality and developmental competence in D-gal-induced aging mice could be rescued by PC.
A. Morphology of oocytes at the GV stage, 14 hours after in vivo maturation and 14 hours after in vitro maturation. Arrows and triangles indicate morphologically abnormal oocytes after in vivo and in vitro maturation, respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm. B. There were no significant differences in terms of oocyte numbers per mouse before or 14 hours after hCG injection in the control, D-gal, and D-gal+PC groups. C. The percent of oocyte polar body extrusion was decreased in D-gal-induced aging mice. This inhibition was reversed by PC. D. D-gal-induced aging increased the percentage of oocyte fragmentation. This was decreased by PC administration after in vivo or in vitro maturation. E. D-gal-induced aging induced oocyte aneuploidy, which was decreased by PC after in vivo or in vitro maturation. Data are presented as the means ± SEMs and were processed by one-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post hoc tests. Significant differences between groups, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. n indicates the number of mice for each treatment.