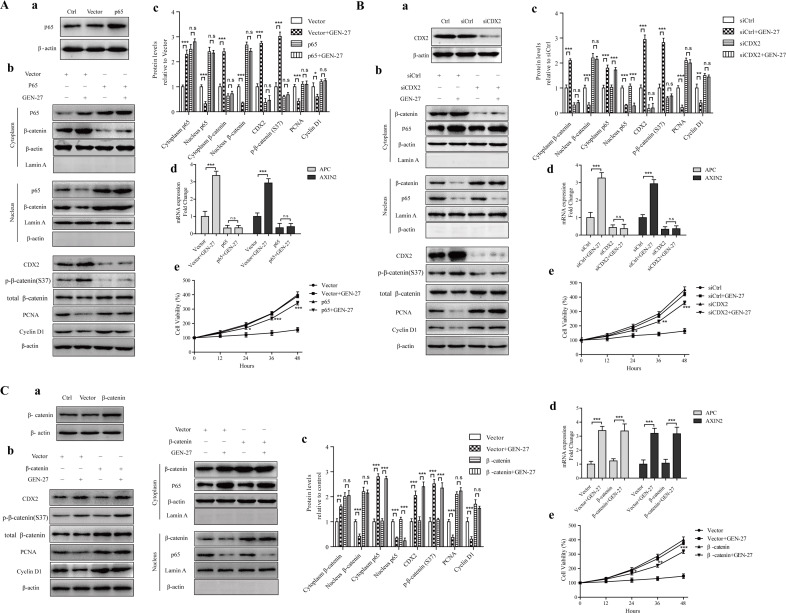
Figure 3. The p65-CDX2-β-catenin axis is responsible for the anti-proliferation effect of GEN-27 on HCT116 human colon cancer cells.
(Aa, Ba, Ca) Protein levels of p65 (Aa), CDX2 (Ba) and β-catenin (Ca) with or without p65 overexpression A., CDX2 silencing B., β-catenin overexpression C. (Ab-c, Bb-c, Cb-c) NF-κB/p65, β-catenin nuclear translocation and protein levels of CDX2, p-β-catenin(S37), total β-catenin, PCNA, and Cyclin D1 were determined by western blot. Data shown are representative of 3 experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01,***P < 0.001. (Ad, Bd, Cc) Real-time qPCR analysis of APC and AXIN2 in HCT116 cells. Values are the mean ± SD (n = 5). (Ae, Be, Ce) Cell viability of HCT116 human colon cancer cells at the indicated time points from each group was analyzed by MTT assay. Each point represents mean ± SD (n = 5). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01,***P < 0.001 vs. p65+GEN-27 group (Ad), siCDX2+GEN-27 group (Bd), or β-catenin+GEN-27 group (Cd). GEN, genistein; GEN-27, genistein-27.