Figure 5. L-FABP-promoted VEGF-A expression is regulated by HIF-1α via the Akt/mTOR/P70S6K/4EBP1 pathway.
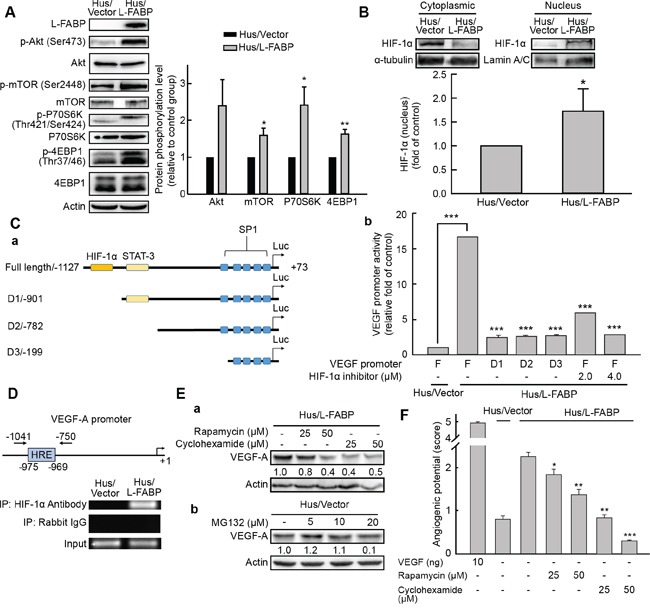
A. Phosphorylation of Akt (Ser473), mTOR (Ser2448), P70S6K (Thr421/Ser424), and 4EBP1 (Thr37/46) in Hus/L-FABP and Hus/Vector (vector-only control) cells analyzed by western blotting. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 versus Hus/Vector control. B. Nucleus and cytoplasmic localization of HIF-1α in Hus/L-FABP cells. Loading controls were α-tubulin and lamin A/C for cytoplasm and nucleus, respectively. HIF-1α levels increased ~1.7-fold in Hus/L-FABP relative to the control group: *p < 0.05. C. a: Diagram of the receptor constructs for the full-length VEGF-A promoter and deletion mutants (D1-D3). b: The luciferase activity of cell extracts was analyzed using a luciferase reporter assay (bar graph). ***p < 0.001 versus Hus/Vector control. D. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay was performed to determine the amount of HIF-1α binding to the VEGF-A promoter; rabbit IgG served as a negative control, and the input served as a positive control. E. a: Western blot analysis of Hus/L-FABP cells treated with rapamycin (mTOR inhibitor: 25 or 50 μM) or cyclohexamide (translation inhibitor: 25 or 50 μM) for 12 h. b: Hus/Vector cells treated with MG132 (proteasome inhibitor: 5, 10, or 20 μM) for 24 h. F. In vitro angiogenic activity (score: see In vitro tube formation assay in Methods for details) of Hus/L-FABP and Hus/Vector cells treated with rapamycin or cyclohexamide (doses identical to those in D) for 12 h. ***p < 0.001 versus Hus/Vector control.
